What is Hangxiety?
Post-drinking guilty feelings accompanied by stress and anxiety have come to be known as “hangxiety.” But what exactly causes hangxiety? Hangxiety is a term that describes the feeling of anxiety or stress people might feel after drinking too much alcohol.
It is caused by a hangover that can linger even after the effects of the alcohol have worn off. Symptoms of hangxiety include guilt, anxiety, irritability, depression, and mood swings. It is vital to practice responsible drinking and seek help if you have a problem with alcohol consumption.
Looking for help with alcohol use disorder challenges like hangovers and anxiety? Join thousands of clients who trusted We Level Up NJ for alcohol and other substance abuse treatments. Call 24/7 for more alcohol rehab information today. Your call is free and confidential. Access addiction professionals who understand your circumstances and are ready to help.
How Long Does Hangxiety Last?
How long does an anxiety hangover last? The duration of its effects on hangxiety varies depending on the individual and how their bodies react to alcohol. Hangxiety can linger 14 to 16 hours after the first hangover symptoms. So, while the hangover anxiety may not stay long, it is not always the case. Anxiety can also persist for 3 to 7 days in those addicted to alcohol.
| How Long Does Alcohol Anxiety Last? | Hangxiety Symptoms |
| Immediate Hangover (0-24 hours) | Hangxiety typically sets in shortly after waking up with a hangover. During this time, you may experience anxiety, regret, and discomfort. This phase can last anywhere from a few hours to the entire day after drinking. |
| Peak Hangxiety (12-24 hours) | Hangxiety peaks during the first day after drinking. This is when feelings of anxiety and unease are often at their strongest. It can make you feel on edge, guilty, or socially awkward. |
| Subsiding Hangxiety (24-48 hours) | As your body continues to recover from the effects of alcohol, hangxiety usually starts to subside. The severity of symptoms begins to lessen, and you may start to feel more like yourself. |
| Complete Recovery (48+ hours) | Often, hangxiety completely dissipates within 48 to 72 hours after heavy drinking. As your body rehydrates, restores its electrolyte balance, and metabolizes the alcohol, you should gradually return to your average mind. |
What Causes Hangxiety?
Why do I get hangxiety? Hangxiety is an unofficial, non-medical term for hangover anxiety, but it’s still accurate. In more official terms, hangover anxiety or hangxiety is a symptom of alcohol withdrawal. While withdrawal is often thought of as something that happens after someone who drinks heavily stops suddenly, it can also occur on a milder scale after just one long night of drinking. If you have a history of depression and anxiety, alcohol will also worsen it.
What causes hangover anxiety? The reason this happens all has to do with alcohol’s impact on the brain. Alcohol intake changes brain chemicals such as serotonin levels, which regulate mood and anxiety. Though alcohol depresses the central nervous system and can have a calming effect initially, pressure can spike back up when those feel-good effects go away. So, even though a few strong drinks might put your mind at ease for a night, you may get bombarded with dread and regret when you wake up the following day.
How To Deal With Hangxiety?
Prevention is often the best strategy for dealing with hangxiety. Drinking in moderation, staying hydrated, and being mindful of your alcohol intake can go a long way in preventing hangovers and their associated anxiety.
How To Prevent Hangxiety?
How to get rid of hangxiety fast? And what is the best hangxiety cure for hangover anxiety? There are ways to prevent hangover anxiety. A list of possible hangover anxiety or hangxiety cure methods include:
- Keep a log of anxiety episodes that follow drinking. This may help you understand whether certain situations or quantities of alcohol cause you stress.
- Drink plenty of water. Hydrate during and after alcohol consumption and avoid coffee and other stimulants that may enhance anxiety.
- Do not drink too quickly. Try to stick to one alcoholic drink per hour. If you tend to drink soon, try enjoying a simple drink on the rocks better suited for sipping. The more alcohol you drink in a short period, the worse the hangxiety will be.
- Avoid drinking alcohol on an empty stomach. Have a snack or quick meal before drinking.
- Only drink with trusted friends. Avoid people and places that may encourage the behavior you regret the next day. You may also prevent hangover anxiety by reducing or eliminating alcohol.
- Set yourself a limit. When you are in the moment and having fun, you may feel fine to keep drinking. However, those drinks will eventually catch up to you. Set a limit and stop drinking when you’ve reached that limit.
How to relieve hangover anxiety? The best thing for hangover anxiety is getting enough food, water, and sleep while taking over-the-counter medicine, if necessary.
Get addiction counseling that works. Discover professional help from We Level Up New Jersey’s addiction and mental health therapists. Start getting support with a free call to our addiction hotline.
Why Do Hangovers Cause Anxiety?
Are you feeling hangxiety? Hangxiety or hangover anxiety is a natural phenomenon. However, some of the common risk factors are:
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Lack of hydration.
- Low tolerance to alcohol.
- Mixing different types of alcohol.
- Lack of sleep.
- Underlying mental health issues.
- Stress or anxiety.
- Poor overall health.
- Lack of food consumption while drinking.
- Genetic predisposition.
Hangxiety describes the anxiety some individuals feel after binge alcohol drinking. Many people know the feeling firsthand. The sense of dread comes from suffering from a hangover while feeling anxious or even ashamed of your activities the night before. It’s often caused by dehydration, exhaustion, guilt, and other emotional and physical effects from drinking. It’s essential to be aware of how your body feels after drinking, as this can help you to be more mindful of any anxious feelings or physical symptoms the next day.
What Helps Hangxiety?
When you experience hangxiety often because you are drinking regularly, it’s time to do something. You can start by speaking to your doctor about it, as they can recommend various treatment methods, including therapy or medication. If you don’t feel comfortable talking with your primary care provider about this, many other options and resources exist for getting sober.
For those experiencing hangxiety often, the first thing to do is stop drinking, as alcohol is why you have hangxiety. Some people can quit drinking entirely on their own or with the help of their family and friends.
One of the best ways to guarantee success is by contacting treatment professionals with experience helping people get clean and sober. Depending on the severity of your addiction, inpatient care may be your best option. Hangxiety treatment may include prescribed medication from a medical professional as well as getting enough food and water.
In-Depth Hangxiety Meaning
The hangxiety definition stems from a combination of the terms “hangover” and “anxiety,” “Hangxiety” refers to the experience of feeling the physical effects of alcohol that are related to a hangover (headache or stomach ache, tiredness, nausea, etc.), compounded by psychological uneasiness. It is the feeling of being “on edge” after drinking. It is also the feeling that “something’s not right” and being paranoid or flat-out scared and can’t explain why.
Hangxiety is a phenomenon that can happen occasionally or more regularly, as it can be connected to several factors. The most common reason (and obvious) is reduced dopamine secretion. Known as the “happy hormone,” dopamine is produced by the brain and used to send messages among nerve cells, regulating our anxiety levels. And the more significant the alcohol consumption, the greater the drop in dopamine, which can lead to feelings of anxiety.
Cortisol may also play a role in the emergence of feelings of “hangxiety.” Unlike dopamine, this hormone, linked with carbohydrate regulation, can increase stress if secreted too large. Excessive alcohol intake will lead to an overproduction of cortisol and may, therefore, lead to stress and anxiety.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- What are Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms? Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome Symptoms. Treatment for the Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal. Stages of Withdrawal Symptoms from Alcohol. Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Timeline.
- How Long Does Alcohol Withdrawal Last? Timeline and Treatment
- Effects of Alcohol Withdrawal
- Does Alcohol Help Anxiety?
- Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Guide. General Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Timeline. Mild to Severe Timeline of Alcohol Withdrawal. Alcohol.Withdrawal Timeline Recovery. Alcohol Withdrawal Symptom Timeline in Detox.
- Alcohol Detox Symptoms, Timeline, & Treatment
- How Long Does it Take to Detox from Alcohol?
- Inpatient Alcohol Rehab Treatment Levels of Care, Therapy Types, and Detox Programs
- Anxiety Medication and Alcohol
- Guide to Signs of Alcoholism. Early Signs of Alcoholism. Signs of an Alcoholic. Signs of Alcohol Poisoning. Signs of Alcohol Withdrawal & Signs of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.
Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Infographic
Alcohol withdrawal can cause anxiety as one of its common symptoms. When a person consuming alcohol regularly and heavily suddenly stops or significantly reduces their alcohol intake, their body and brain undergo various physiological changes. These changes can lead to a range of withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety.
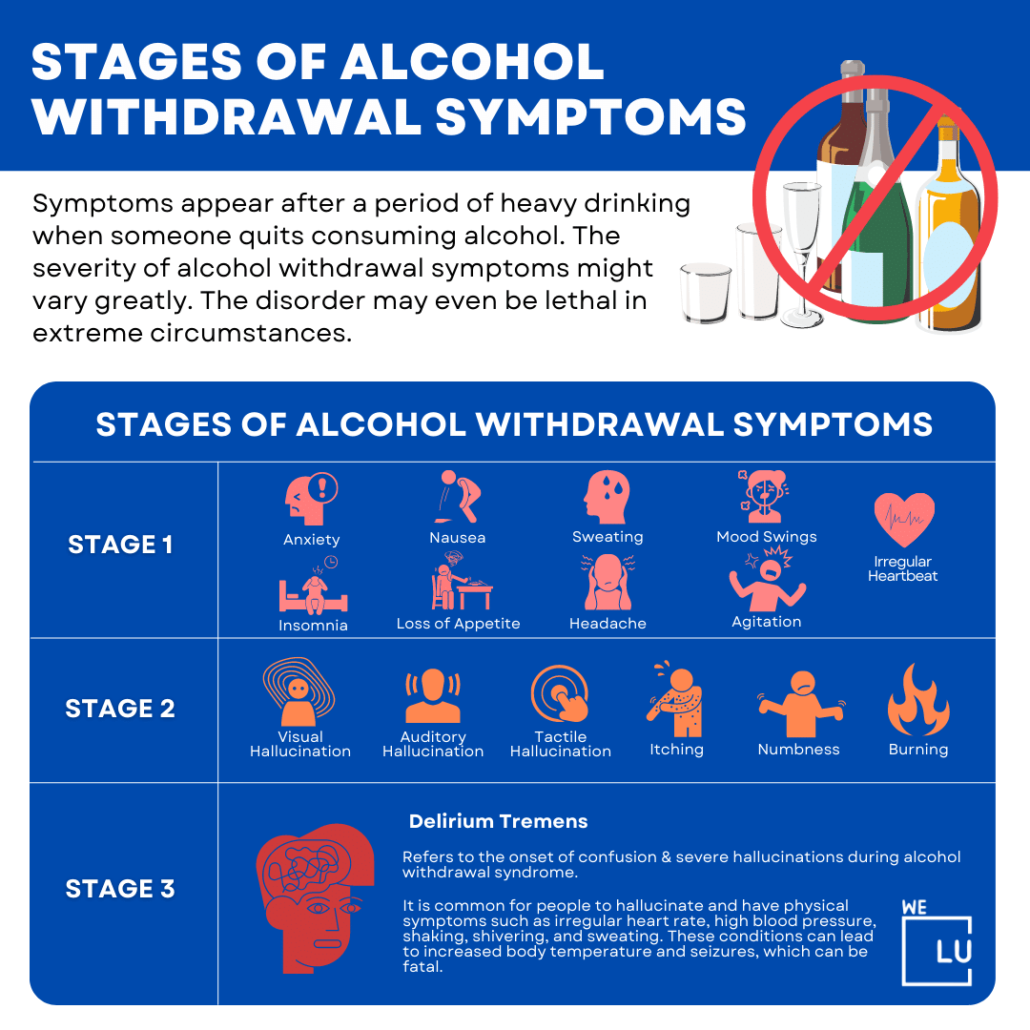
Embed the above “Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms” Infographic to your Website. The We Level Up NJ addiction treatment center team provides this alcohol withdrawal infographic. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/hangxiety/
Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms infographic image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Stages-Of-Alcohol-Withdrawal-Timeline-1-1030×1030.png
Hangover Anxiety Symptoms Chart
Experiencing hangxiety for days? Some people have had Hangxiety that lasts for days. The uneasiness associated with a hangover lasts as long as it takes the body to restore normal chemical levels. If you find your hangxiety is lasting longer than a day, you need to make an appointment with your doctor. Chronic stress from hangovers and anxiety can significantly damage your health and quality of life.
While hangxiety is commonly associated with alcohol, it can also occur after using various substances, including drugs. The term “hangxiety” is often used more broadly to describe the feelings of anxiety, unease, or remorse that can follow the use of substances like:
| Substance | Potential Hangover Symptoms Anxiety |
| Adderall Hangover | Anxiety, restlessness, irritability, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. |
| Ambien Hangover | Anxiety, confusion, memory problems, dizziness, feeling “hungover.” |
| Ativan Hangover | Anxiety, drowsiness, difficulty with coordination, memory impairment, decreased alertness. |
| Meth Hangover | Unlike benzo hangovers, meth can cause intense anxiety, paranoia, agitation, fatigue, irritability, depression. |
| Gabapentin Hangover | Anxiety, dizziness, drowsiness, unsteadiness, memory problems. |
| Klonopin Hangover | Anxiety, drowsiness, impaired coordination, slurred speech, difficulty concentrating. |
| Valium Hangover | Anxiety, drowsiness, muscle weakness, confusion, memory problems. |
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug & Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You? Or Mental Health Support?
Even if you have failed previously, relapsed, or are in a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. Call us when you feel ready or want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7Hangxiety Symptoms
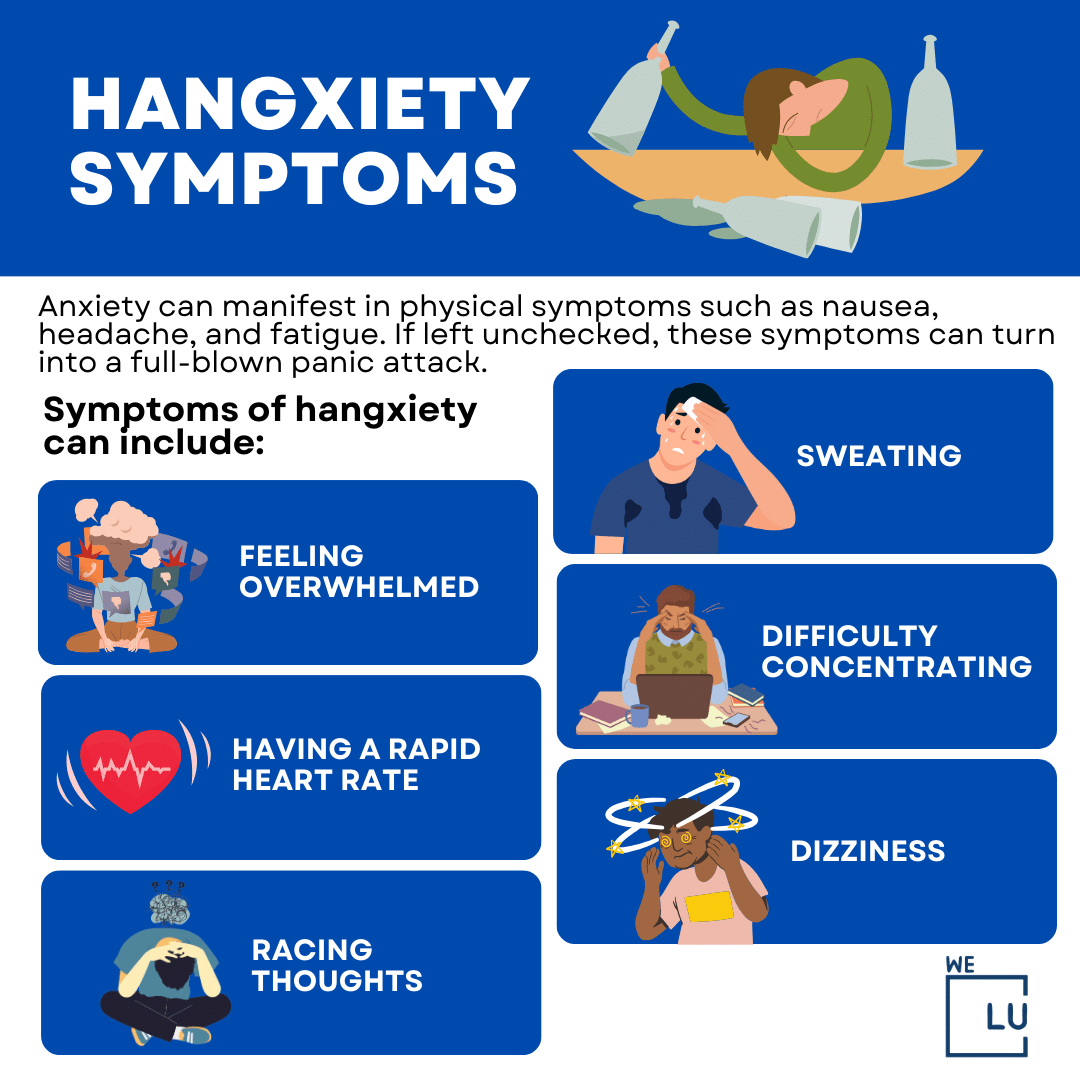
Anxiety can manifest in physical symptoms such as nausea, headache, and fatigue. If left unchecked, these symptoms can turn into a full-blown panic attack.
Symptoms of hangxiety can include:
- Feeling overwhelmed.
- Having a rapid heart rate.
- Racing thoughts.
- Sweating.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Dizziness.
Hangxiety can also involve guilt or shame about not being productive or feeling like you “should” be able to do more. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by these feelings, it can be helpful to break tasks down into smaller pieces or take breaks during the day to give yourself a chance to rest and rest. Reaching out to friends, family, and professionals who can help provide support and guidance can also be beneficial.
Hangxiety is not only a physical reaction but can also have psychological triggers. People who have had a past traumatic experience while under the influence of alcohol can have lingering feelings of anxiety triggered by drinking. These feelings can be further exacerbated if the individual is not surrounded by a supportive community or network of friends or family.
Does alcohol help anxiety? Heavy drinking causes an influx of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), making a person feel calm and relaxed. This becomes a “crutch” for chronic drinkers. When alcohol is taken out of the picture, and the effects of alcohol withdrawal kick in, GABA is no longer present. Thus, the feeling of calmness is also taken away, leading to hangxiety.
Alcohol Anxiety
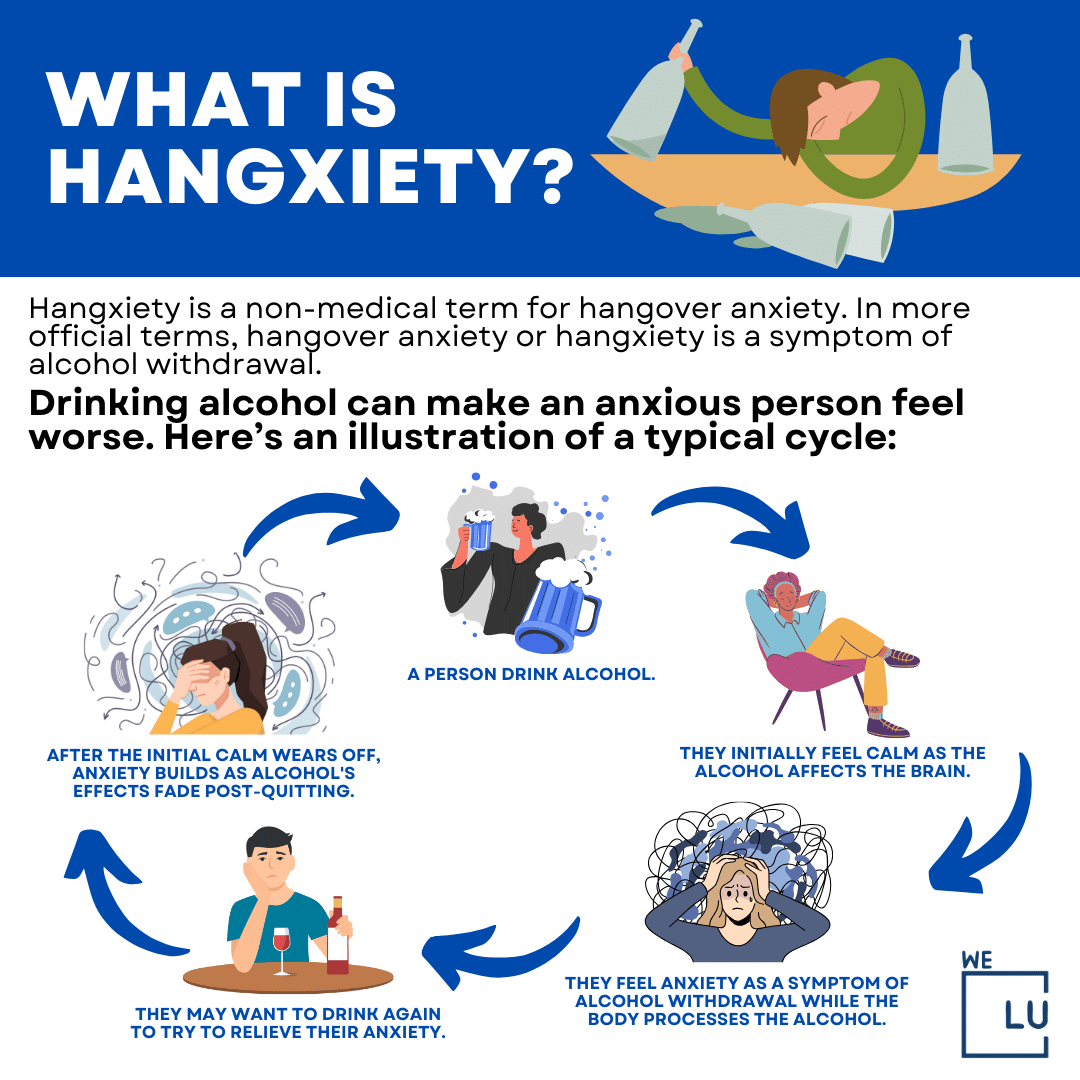
The co-occurrence of alcohol and anxiety disorders is relatively prevalent. The research found that 20% of those with social anxiety have an alcohol misuse problem. The abuse of alcohol and anxiety often make each other significantly worse. This is especially problematic as the two are often closely linked. How to help hangxiety? As with many dual-diagnosis conditions, alcoholism and anxiety commonly exist together within the same person. Anxiety is a reason many people drink and a result of drinking. It becomes a vicious cycle. Drinking alcohol can make an anxious person feel worse.
Here’s an illustration of a typical cycle:
- A person drinks alcohol.
- They initially feel calm as the alcohol affects the brain.
- They feel anxiety as a symptom of alcohol withdrawal as the body processes the alcohol.
- They may want to drink again to try to relieve their anxiety.
- But this only starts the process from the origin. As the initial calming effect disappears, the person can feel anxiety after quitting drinking alcohol builds again as the effects wear off.
The more alcohol consumed, the greater the tolerance will be. Over time, there is a need to drink more alcohol to feel the same effects. Over time, this may negatively affect mental health, resulting in higher anxiety and depression after drinking. Anxiety disorder makes an individual start drinking alcohol, which worsens their fear, leads them to drink more, and deepens their concern. It’s a never-ending vicious cycle of alcohol and stress.
Top 10 Most Frequently Asked Questions About Hangover and Anxiety
-
Why do I get anxiety after drinking?
Anxiety after drinking can occur due to the depressant effects of alcohol wearing off, leading to heightened activity in the central nervous system and changes in neurotransmitter levels, including a decrease in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which promotes relaxation and an increase in glutamate, which can lead to anxiety and overstimulation. Moreover, alcohol’s impact on brain chemistry, personal tolerance, and psychological factors can all contribute to post-drinking stress.
-
Is a hangover alcohol withdrawal?
A hangover is not the same as alcohol withdrawal, although they can share some symptoms. A hangover typically occurs as a result of the immediate aftereffects of drinking alcohol, such as dehydration, disrupted sleep patterns, and the presence of toxins in the body, while alcohol withdrawal refers to a more severe set of symptoms that can occur when a person who is physically dependent on alcohol stops drinking abruptly, often involving a range of physical and psychological symptoms, including anxiety, tremors, and in severe cases, seizures or hallucinations.
-
How to stop your heart racing when hungover?
To help stop your heart racing when hungover, focus on hydration by drinking water or electrolyte-rich beverages to replenish lost fluids and balance electrolytes. Also, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation to help calm your nervous system and reduce anxiety, which can contribute to an elevated heart rate during a hangover.
-
How to get rid of hangover anxiety?
To alleviate hangover anxiety, hydrate to combat dehydration, which can worsen anxiety. You can also consider taking over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen, practicing relaxation techniques, and getting plenty of rest to help reduce anxiety symptoms associated with a hangover.
-
How long does hangover anxiety last?
The duration of hangover anxiety can vary widely depending on factors like the amount of alcohol consumed, individual tolerance, and overall health. In most cases, hangover anxiety peaks within the first 24 hours after drinking and typically subsides within 48 to 72 hours as the body recovers and processes the alcohol.
-
Does Adderall help with hangovers?
Adderall is not a recommended remedy for hangovers. While it may temporarily counteract the fatigue associated with a hangover due to its stimulant effects, it can also exacerbate anxiety and other hangover symptoms and is generally not considered a safe or practical solution.
-
Can I take Klonopin after a night of drinking?
It is not advisable to take Klonopin (clonazepam) after a night of drinking. Combining alcohol with Klonopin can lead to dangerous interactions, including increased sedation, impaired coordination, and a heightened risk of accidents or overdose. If you’re experiencing anxiety or discomfort after drinking, it’s best to seek alternative remedies or consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
-
How to sleep with hangover anxiety?
To sleep with hangover anxiety, try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation to calm your mind and reduce stress. Also, create a comfortable sleep environment by dimming the lights, maintaining a cool room temperature, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol, which can disrupt sleep.
-
How to get rid of melatonin hangover?
If you’re experiencing a “melatonin hangover” or grogginess from taking melatonin supplements, adjusting the dosage is the best way to mitigate it. Start with a lower dose (typically 1-3 mg) and take it at least 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime to allow gradual onset. If you still feel groggy in the morning, consider reducing the dosage further or consulting a healthcare professional for guidance.
-
How long does a panic attack hangover last?
The duration of a panic attack “hangover,” which refers to the residual physical and emotional effects after a panic attack, can vary from person to person. It often lasts a few hours to a day, during which individuals may feel fatigued, emotionally drained, and experience residual anxiety or unease.
What is Hangover Anxiety? Fact Sheet
Hangover vs Withdrawal
Hangover and withdrawal are two distinct physiological responses associated with the use of substances, but they have some key differences:
Hangover or Withdrawal
Alcohol Hangover
- Cause: Hangovers occur due to the immediate aftereffects of consuming a substance, most commonly alcohol. They are the body’s reaction to the toxins in alcohol and the impact of alcohol on various bodily functions.
- Onset: Hangover symptoms typically begin within hours after drinking, usually the morning after a night of heavy drinking.
- Duration: Hangovers are usually short-term and temporary, typically lasting for up to 24 hours but sometimes longer, depending on the amount of alcohol consumed and individual factors.
- Symptoms: Hangover symptoms can include headache, nausea, vomiting, dehydration, fatigue, irritability, and sensitivity to light and sound. Anxiety can also be a component of a hangover, often referred to as “hangxiety.”
- Treatment: Hangovers are generally managed through rest, hydration, over-the-counter pain relievers, and time.
Alcohol Withdrawal
Alcohol Withdrawal and Anxiety
- Cause: Withdrawal occurs when a person physically dependent on a substance, such as alcohol, drugs, or medications, stops using it or significantly reduces their intake. Withdrawal is the body’s response to the absence of the substance.
- Onset: Withdrawal symptoms typically begin within hours to days after the last use of the substance, depending on the substance and the individual’s level of dependence.
- Duration: Withdrawal can last for several days to weeks and, in some cases, even longer. The time and severity of withdrawal symptoms vary widely.
- Symptoms: Withdrawal symptoms can vary widely depending on the substance but often include anxiety, tremors, sweating, nausea, insomnia, irritability, and, in severe cases, hallucinations or seizures.
- Treatment: The management of withdrawal often requires medical supervision, especially in cases of severe withdrawal. Treatment may include medications, counseling, and support to help individuals safely detox and manage withdrawal symptoms.
Hangovers result from acute substance use and are short-term. At the same time, withdrawal occurs when someone is physically dependent on a substance and stops using it, with symptoms that can be more severe and longer-lasting. Alcohol withdrawal often necessitates medical intervention, whereas hangovers can typically be managed with rest and self-care.
Hangxiety Symptoms
Symptoms of hangxiety vary from individual to individual, like with all other illnesses and disorders. Some of the common signs and symptoms of hangxiety are as follows:
- Fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Thirst.
- Headache.
- Muscle ache.
- Nausea.
- Stomach pain.
- Vertigo.
- Light and sound sensitivity.
- Irritability.
- Anxiety.
- Paranoia.
- Sweating.
- Increased blood pressure.
How To Reduce Hangover Anxiety?
How to ease hangover anxiety? While hangover symptoms vary from person to person, one of the most common complaints hangover sufferers have is a feeling of “anxiety.” Anxiety is a normal reaction that we all have to new or powerful stimuli in our lives.
When we feel anxious, we must remember it is an appropriate response. However, the problem is that when the hangover sets in, and our brain is confused, it may lead to an overreaction to these stimuli, leading to anxiety.
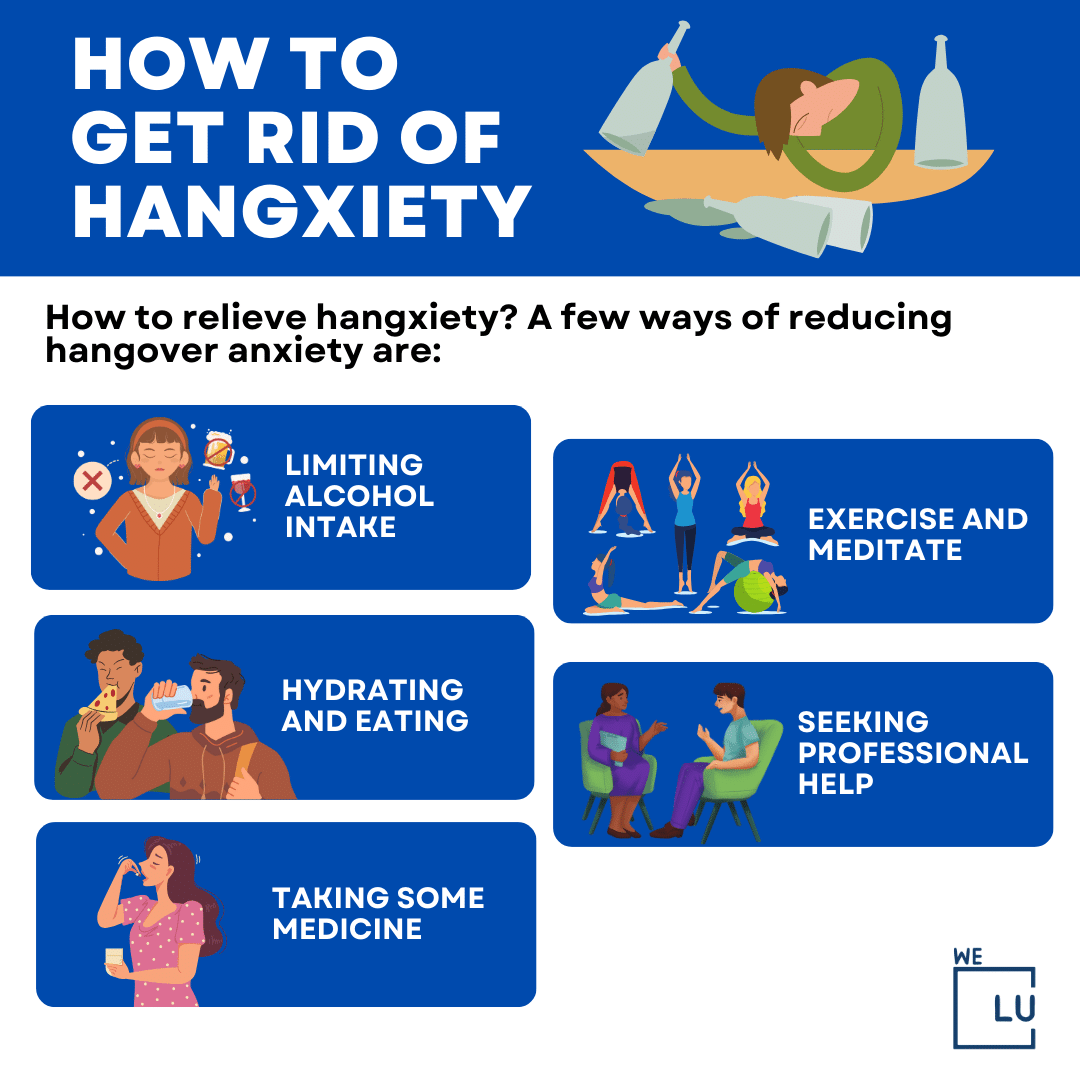
How to relieve hangxiety? A few ways of reducing hangover anxiety are:
- Limiting alcohol intake.
- Hydrating and eating.
- Taking some medicine.
- Exercise and meditate.
- Seeking professional help.
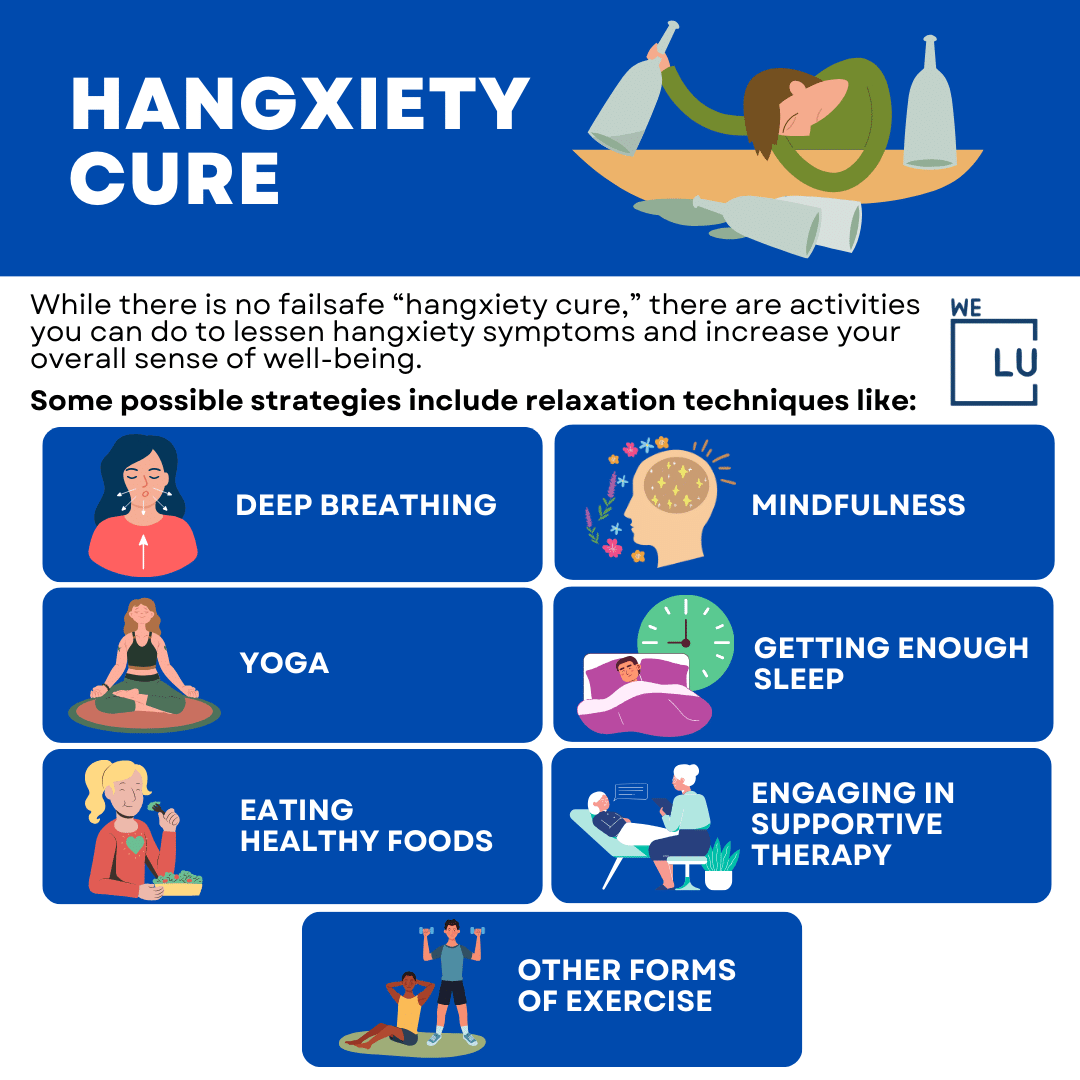
Hangxiety Cure
How do you get rid of hangxiety? While there is no failsafe “hangxiety cure,” there are activities you can do to lessen hangxiety symptoms and increase your overall sense of well-being. Some possible strategies include relaxation techniques like:
- Deep breathing.
- Mindfulness.
- Yoga.
- Other forms of exercise.
- Getting enough sleep.
- Eating healthy foods.
- Engaging in supportive therapy.
How To Stop Anxiety After Drinking Alcohol?
You can try a few things to stop anxiety after drinking alcohol. To prevent stress after drinking alcohol, try to:
- Take deep breaths: Take slow, deep breaths to help calm your body and mind.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Try progressive muscle relaxation or mindfulness meditation to help you relax.
- Get some exercise: Physical activity can help reduce anxiety and improve your mood.
- Try to get some sleep: Getting a good night’s sleep can help you feel more rested and refreshed, which may help reduce anxiety.
- Talk to someone: Sometimes, talking about your feelings can be helpful. Consider talking to a friend, family member, or mental health professional.
- Drink plenty of water: Alcohol can cause dehydration, which can contribute to feelings of anxiety. Drinking water can help hydrate your body and may help reduce stress.
- Consider taking medication: If your anxiety is severe or persists despite trying other methods, your healthcare provider may recommend medication to help reduce your stress.
Emotional Hangover Meaning
An “emotional hangover” is a colloquial term to describe the lingering emotional effects or consequences of a particularly intense or emotional experience. Just as a physical hangover is characterized by discomfort and symptoms following heavy drinking, an emotional hangover refers to the psychological and emotional impact that lingers after an intensely emotional event or intense experience.
These emotional hangovers can manifest as a wide range of feelings, such as sadness, anxiety, exhaustion, or even euphoria, depending on the nature of the event. They can also affect cognitive functioning and decision-making, making it difficult for individuals to process their emotions or make rational decisions fully. While “emotional hangover” is not a clinical term, it highlights that powerful emotions can impact a person’s mental and emotional state.
Drinking alcohol can raise the risk of developing anxiety and additional mental health issues. Suppose you’re struggling with anxiety and alcohol use and don’t know how to stop anxiety after drinking. In that case, seeking help from a mental health professional or substance abuse treatment program may be helpful.

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care at the We Level Up Treatment Centers Network.
Hotline (877) 378-4154Alcohol and Anxiety Statistics
Alcohol use disorder and anxiety are frequent co-occurring disorders that can be highly distressing and hurt daily functioning. A pre-existing anxiety disorder can also influence an alcohol use disorder because it can worsen it, cause new anxiety symptoms, or have the opposite effect (as many individuals use alcohol as an unhealthy coping mechanism).
85.6%
In 2019, 85.6% of people said they had drunk alcohol at some point.
Source: NIAAA
25%
25% of those who sought treatment for panic disorder also had a history of alcoholism.
Source: Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
7.2%
People with alcohol use disorder aged 12 and older received treatment 7.2% of the time in the previous year.
Source: NIAAA
Best Hangxiety Cure Pills
Your doctor may be open to offering you the best hangxiety pills medications on the market. A doctor may prescribe hangxiety pills such as Duloxetine (Cymbalta), escitalopram (Lexapro), or paroxetine as antidepressants (Paxil). He or she may prescribe alprazolam (Xanax), Diazepam (Valium), and Lorazepam when it comes to benzodiazepines (Ativan). Each type of anxiety medication acts uniquely. To find out which drug is best for you, visit your doctor.
Several of these drugs may interact with alcohol. Before taking any of these medications, discuss your alcohol use with your doctor since side effects can be severe or fatal. Alcohol-induced anxiety, hangxiety, can be reduced by changing one’s lifestyle. Alcohol anxiety can be treated but not permanently cured.
Xanax for Hangover
How to stop hangxiety? If you have been prescribed Xanax for hangxiety, you should not drink alcohol to prevent worsening anxiety, especially if you take Xanax and alcohol simultaneously. Alcohol and Xanax hangovers can have many adverse effects, like difficulty breathing. Other alternatives to Xanax do not result in difficulty breathing and death if you drink alcohol.
Ativan for Hangover Anxiety
Lorazepam for hangover anxiety? Lorazepam, commonly called Ativan, is a prescribed drug that can be abused. Alcohol is one of the drugs that is frequently used along with benzodiazepines like Ativan. Since both Ativan and wine, or other types of alcohol, depress the nervous system, combining them can be fatal and result in decreased breathing, profound sleepiness, coma, and death. If Ativan has been prescribed, you might want to avoid alcohol.
Ativan hangover symptoms may include the following:
- Insomnia.
- Fatigue.
- Increased pulse.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Increased body temperature.
- Excessive sweating.
Valium for Hangover
Valium is a medication used to treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and seizures, so it is not safe to take Valium as a recreational drug and consume liquid Valium drink occasionally. The risk is not just from alcohol but also the drug interaction between the two.
If you are experiencing a Valium hangover, you should be cautious of operating machinery. The primary benefit of taking Valium is that it gives you a sense of less anxiety. However, the immediate risk is that you will increase your breathing difficulties by taking Valium with alcohol.
Other medications like Lexapro alcohol hangovers, Sertraline and alcohol hangovers, Cymbalta and alcohol hangovers, and Zoloft and alcohol hangovers are effective at dealing with Hangxiety.
How To Get Rid of Hangxiety Fast?
How to cure hangover anxiety? Counseling, such as hangover supportive therapy, maybe the most effective strategy to reduce stress if you suffer from social anxiety or phobia (combined with a medication such as Sertraline or Zoloft). Suppose you have a generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), marked by an unexplainable sensation of concern or tension. Your doctor may recommend cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) or discussing your anxiety with a therapist.
Do you have questions about post alcohol anxiety or treatment in general? Call our helpline 24/7.
Top 10 Most Common FAQs About the Best Medication for Hangover
-
What is the best food for hangover anxiety?
The best foods for hangxiety, or anxiety when hungover, help replenish nutrients and stabilize blood sugar levels. Opt for a balanced meal with complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and fruits or vegetables. Foods like whole-grain toast with eggs and avocado or a smoothie with banana, spinach, and protein can help provide essential nutrients and promote recovery from a hangover, which in turn can alleviate anxiety.
-
Can I take Gabapentin for hangovers?
Gabapentin is not typically recommended as hangxiety pills. While it is a medication used for various medical conditions, it should be directed by a healthcare professional for specific purposes, and it’s not considered a standard remedy for dealing with hangovers. If you’re experiencing severe or persistent symptoms of anxiety days after drinking, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for guidance on managing hangover symptoms or addressing any underlying concerns.
-
Why do I have anxiety after drinking?
Anxiety and panic attack hangover for days can be attributed to several factors. Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant, and when its effects wear off, it can lead to heightened anxiety and restlessness as the brain and body attempt to return to a state of equilibrium. Also, alcohol can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, particularly affecting gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate, contributing to anxiety during and after drinking. Finally, individual factors like tolerance, personal susceptibility to stress, and the quantity and type of alcohol consumed can all influence the presence and intensity of post-drinking anxiety.
-
What are OTC meds for hangovers?
Over-the-counter (OTC) hangover anxiety pills primarily focus on relieving specific symptoms associated with hangovers, such as headache, nausea, and dehydration. Standard OTC options include pain relievers like ibuprofen or aspirin for headaches, antacids for stomach discomfort, and rehydration solutions or electrolyte-rich drinks to combat dehydration. However, it’s essential to use OTC medications as directed and not exceed recommended dosages, as misuse can have adverse effects and may not address all anxiety after drinking alcohol.
-
Do shrooms give you a hangover?
Psilocybin mushrooms (called “shrooms”) do not typically give users a traditional hangover like alcohol or certain drugs. Instead, after the effects of the psychedelic experience wear off, some individuals may experience a period of mental and emotional fatigue, often referred to as a “post-trip” or “afterglow” state, but this is generally not characterized by physical discomfort or symptoms commonly associated with hangovers. In worst cases, an anxiety attack hangover from shrooms may refer to stress after a “bad trip.”
-
Does Adderall help hangovers?
Adderall is not recommended as a hangover anxiety cure. While it may temporarily counteract the fatigue associated with a hangover due to its stimulant effects, it can also exacerbate other hangover symptoms, such as anxiety, dehydration, and increased heart rate. It is generally not considered a safe or effective solution for relieving hangover symptoms.
-
How to recover from a panic attack hangover?
Recovering from panic attacks days after drinking involves prioritizing self-care and emotional well-being. Focus on rest, hydration, and calming activities like deep breathing, meditation, or gentle exercise to help your body and mind recover. Also, consider seeking support from a therapist or counselor to address the underlying causes of the panic attack and develop strategies for managing anxiety in the long term.
-
Is hangxiety real?
Yes, “hangxiety” is an actual term to describe the anxiety or unease some people experience after a night of heavy drinking, often associated with a hangover. This phenomenon can happen as anxiety the day after drinking, severe anxiety after drinking, and anxiety after a night of drinking. It is recognized by many individuals who have experienced it and is supported by research on the psychological and physiological effects of alcohol consumption.
-
How to cure hangxiety?
Alcohol anxiety cure and hangover depression cure must address the immediate symptoms and underlying causes. In the short term, focus on hydration, nutrition, rest, and relaxation techniques to alleviate anxiety. Consider moderating alcohol consumption, managing stress, and seeking support from a healthcare professional or therapist to address any underlying mental health concerns contributing to hangxiety and hangover guilt (feelings of guilt after drinking).
-
How long does therapy hangover last?
A “therapy hangover” is not a recognized medical or psychological term. However, if you mean that you’re experiencing emotional fatigue or vulnerability after a therapy session, this can vary widely from person to person. For some individuals, these feelings may last for a few hours, while for others, they may persist for a day or more. It’s essential to recognize and address these feelings with self-care and support. Still, if they continue or become overwhelming, discussing them with your therapist to gain insight and develop coping strategies is a good idea.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline (877) 378-4154Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
What is Hangxiety? Infographic
The term “hangxiety” refers to the worry and anxiety that follow binge drinking, but what exactly triggers hangxiety? The sense of worry or anxiety that some people experience after consuming too much alcohol is known as hangxiety.
Embed the above “What is Hangxiety?” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/hangxiety/
What is Hangxiety? image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/What-is-Hangxiety-min-1030×1030.png
Embed the above “Hangxiety Symptoms” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/hangxiety/
Hangxiety Symptoms image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Hangxiety-Symptoms-min-1030×1030.png
Embed the above “Hangxiety Cure” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/hangxiety/
Hangxiety Cure image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Hangxiety-Cure-min-1030×1030.png
Embed the above “How to Get Rid of Hangxiety?” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/hangxiety/
How to Get Rid of Hangxiety? image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/How-to-Get-Rid-of-Hangxiety-min-1030×1030.png
How To Get Over Hangxiety?
How to calm hangover anxiety? And how to stop hangover anxiety? While hangxiety can transpire after just one night of drinking, it can also signify that you may be drinking too much. Aside from asking how to sober fast, ask yourself why you’re drinking. How to deal with hangxiety? One criterion for diagnosing an alcohol use disorder is to continue drinking even though it makes you feel depressed or anxious or adds to another health problem. If you are frequently experiencing anxiety and are having trouble cutting back on drinking, it’s worth consulting a medical professional.
There is a strong link between mental health conditions, such as anxiety, and alcohol abuse. Individuals who struggle with mood disorders like anxiety are more susceptible to developing an addiction to drugs or alcohol, often to self-medicate symptoms of their underlying mental health condition. These co-occurring disorders can make each other worse without proper treatment.
How to overcome hangxiety? Are you searching for the best med for hangovers? Accurately assessing all signs and symptoms is crucial to determining the most effective anxiety after drinking cure. When a mental health professional has evaluated the symptoms, it may be determined that another form of mental condition is present and needs a particular treatment.

Medically-Assisted Alcohol Detox
Detox is often considered the first stage of treatment. It will help you navigate the complicated process of alcohol withdrawal but doesn’t address patterns of thought and behavior contributing to alcoholism. Various treatment settings and approaches can help provide the ongoing support required to maintain sobriety long-term after you complete alcohol detox.
Cravings are very expected during alcohol detox and can be challenging to overcome. This often leads to drinking again and relapse. Constant medical care provided during inpatient rehab helps prevent relapse. Clinicians can offer the necessary medication and medical expertise to lessen cravings and the effects of withdrawals.
Psychotherapy for Alcohol and Anxiety
Several different modalities of psychotherapy have been used in the treatment of alcoholism and anxiety, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy – CBT is an effective treatment that involves changing both the patterns of negative thoughts and the behavioral routines that are affecting the daily life of the depressed person for various forms of anxiety and alcohol use disorder.
- Person-Centered Therapy – A strategy that allows and encourages clients to understand and resolve their concerns in a safe, supportive environment.
- Solution-Focused Therapy – An approach interested in solutions that can be quickly implemented with a simple first step leading to further positive consequences.
Overcoming Hangxiety. Find the Support You Need.
Anxiety from drinking alcohol and withdrawal is often challenging to go through alone. Many people experience relapses during withdrawal in an attempt to alleviate symptoms and satisfy cravings. However, you can manage withdrawal symptoms and successfully recover with detox and rehab therapy and a robust support system at the We Level Up New Jersey treatment center. If you require assistance with your rehab journey, contact a We Level Up NJ treatment professional now. Your call is free and confidential.
Get a free rehab insurance check without any obligation.
Dual Diagnosis Programs In New Jersey
Alcohol use disorder and mental health disorders often co-occur. Traumatic experiences, anxiety, and stress can often result in mental health disorders and alcoholism. Dual-diagnosis rehabilitation treats both of these issues simultaneously. The best approach for the treatment of dual diagnosis is an integrated system. This treatment strategy helps treat both the alcohol problem and the mental disorder. Regardless of which diagnosis (mental health or alcohol use disorder) came first, long-term recovery will depend mainly on the detox treatment for both conditions done by the same team or healthcare provider.
Medication-Assisted Treatment for Alcohol
Medication-assisted treatments (MAT) for alcohol and mental health disorders are commonly used in conjunction. This includes the use of pharmaceuticals and other medical procedures. During your alcohol rehab, the staff from your facility will help you distinguish what caused your alcoholism and teach you coping skills that will help you change the patterns of your behavior and challenge the negative thoughts that led to your drinking. Sometimes, the pressures and problems in your life make you rely on substances to help you forget about them momentarily.
Find inpatient rehab in New Jersey that works for you!
Hangover anxiety or hangxiety is a symptom of alcohol withdrawal. The development of alcohol tolerance and withdrawal are indications of alcohol addiction. Contact one of our helpful treatment specialists today if you or a loved one are struggling with long-term addiction and a co-occurring mental health condition such as anxiety and depression. Our New Jersey Level Up rehab center can provide information on dual diagnosis and detox programs that may fit your needs.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL (877) 378-4154End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Top 10 Most Popular How Drinking Affects Anxiety? FAQs
-
Why is my hangover lasting so long?
If your hangover lasts longer than usual, it may be due to various factors, including the amount and type of alcohol consumed, individual tolerance, and overall health. Also, inadequate hydration, poor nutrition, and lack of rest can prolong symptoms of being anxious after drinking, so prioritizing self-care can help alleviate and shorten the duration of a hangover. If your hangover persists for an extended period or becomes a recurring issue, it’s advisable to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying health concerns.
-
Why does hangxiety happen?
Hangxiety, or day after drinking anxiety, can occur due to several factors. Alcohol is initially a depressant that lowers stress. Still, as its effects wear off, it can lead to changes in brain chemistry, including a decrease in the neurotransmitter GABA (which promotes relaxation) and an increase in glutamate (which can cause anxiety and overstimulation). Also, the psychological effects of alcohol, such as regret or embarrassment from the previous night’s activities, can contribute to hangxiety.
-
How long does hangover depression last?
Hangover depression, a typical component of a hangover, generally lasts for a day or two after heavy drinking. However, the duration can vary depending on factors like the amount of alcohol consumed, individual tolerance, and overall health, and for some individuals, it may persist for several days.
-
How to avoid hangxiety?
To avoid hangxiety, practice moderation when drinking alcohol and be mindful of your limits. Hydration is critical, so drink water alongside alcoholic beverages and before going to bed, and consider eating a balanced meal before drinking to slow the absorption of alcohol into your system. Also, manage stress and prioritize self-care to reduce the overall risk of experiencing anxiety after drinking.
-
How to fix hangxiety?
To alleviate hangxiety, focus on self-care and recovery. Start by hydrating, eating a nutritious meal, and getting plenty of rest, as these can help restore your body and mind to balance. Moreover, practice relaxation techniques, like deep breathing or meditation, to ease anxiety, and consider avoiding excessive alcohol consumption or seeking professional support if hangxiety becomes a recurrent issue.
-
How long can hangxiety last?
The duration of hangxiety can vary widely from person to person and depends on factors such as the amount of alcohol consumed, individual tolerance, and overall health. In most cases, hangxiety peaks within the first 24 hours after drinking and typically subsides within 48 to 72 hours as the body processes the alcohol and returns to balance.
-
How to help hangover anxiety?
To help with hangover anxiety, focus on hydration by drinking water or electrolyte-rich beverages to replenish lost fluids and balance your system. Furthermore, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation to calm your mind and reduce anxiety, which can contribute to feelings of unease during a hangover.
-
What is the best alcohol for anxiety?
There is no specific type of alcohol that is universally considered the best for anxiety, as alcohol can exacerbate anxiety symptoms for many people. It’s generally recommended to consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether if you have anxiety, as excessive alcohol consumption can increase anxiety and worsen mental health issues.
-
Can you have a hangover panic attack?
Yes, it’s possible to experience a panic attack during or after a hangover, especially if you are prone to anxiety or have a history of panic attacks. The physical discomfort, dehydration, and changes in neurotransmitter levels associated with a hangover can trigger or exacerbate feelings of anxiety and panic in some individuals.
-
Why does alcohol gives me anxiety?
Alcohol can give you anxiety because it affects neurotransmitters in your brain, including gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate, which play critical roles in relaxation and arousal. As the effects of alcohol wear off, there can be an imbalance in these neurotransmitters, leading to increased anxiety and restlessness. Also, the psychological effects of alcohol, such as regret or social embarrassment, can contribute to anxiety during or after drinking.
How To Sober Up Fast: Top 12 Effective Ways & Tips How To Get Sober Fast Video
Sobriety and alleviating hangxiety take time, as alcohol needs to be metabolized by your body. The most effective way to prevent hangxiety and hangovers is to consume alcohol in moderation or abstain altogether. Excessive alcohol consumption can have adverse effects on both physical and mental health. If you frequently experience hangxiety or have concerns about your relationship with alcohol, consider seeking guidance from We Level Up NJ alcohol use disorder treatment.
Watch the video below for general tips about how to sober up fast!
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers various recovery programs at each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up NJ Hangxiety Detox, Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] NIAAA (National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism) – https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh22-1/38-43.pdf
[2] NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3860396/
[3] NIH (National Institutes of Health)– https://medlineplus.gov/anxiety.html
[4] Acute alcohol sensitivity. (2015).
rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/12634/acute-alcohol-sensitivity
[5] Buckner JD, et al. (2016). Social anxiety and alcohol-related impairment: The mediational impact of solitary drinking.
sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306460316300429?via%3Dihub
[6] Dietary guidelines for alcohol. (2020).
cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/moderate-drinking.htm
[7] Goldstein JL, et al. (2015). Gastrointestinal injury associated with NSAID use: A case study and review of risk factors and preventative strategies.
dovepress.com/gastrointestinal-injury-associated-with-nsaid-use-a-case-study-and-rev-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-DHPS
[8] Hangovers. (2021).
niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/hangovers
[9] Marsh B, et al. (2019). Shyness, alcohol use disorders and ‘hangxiety’: A naturalistic study of social drinkers.
sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0191886918305762?via%3Dihub
[10] Neuroscience: Pathways to alcohol dependence. (2009).
pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/aa77/aa77.htm
