Guide to Ativan
Discover the shocking truth: about 40 million American adults, 18 percent of the population, are plagued by anxiety. Learn about the standard solution, lorazepam, a powerful anti-anxiety medication known as Ativan.
Control anxiety symptoms with Ativan under medical supervision. Relieve panic attacks, sleeplessness, agitation, and restlessness effectively. Treat seizures, spasms, alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia too. Be cautious of potential Ativan side effects, especially from excessive use.
Looking for help with substance abuse challenges like Ativan side effects from excessive use? Join thousands of clients who trusted We Level Up New Jersey for substance abuse treatments. Call 24/7 for more Ativan detox or rehab information today. Your call is free and confidential. Access addiction professionals who understand your circumstances and are ready to help.
Ativan Side Effects and Drug Guide
Ativan side effects can be mild to severe. The below guide lists some critical Ativan side effects that may occur while taking the drug. This list doesn’t include all possible Ativan side effects. Talk with your doctor or pharmacist for more information on the possible Ativan side effects. Find our tips on minimizing troubling Ativan side effects.
Ativan Uses
This medication serves to alleviate anxiety symptoms. It falls within the category of medications referred to as benzodiazepines, which exert their influence on the central nervous system, specifically the brain and nerves, resulting in a soothing effect. Its mechanism of action involves amplifying the impact of a specific naturally occurring chemical in the body, known as GABA.
Ativan (lorazepam) uses, conditions treated, and their dose
Ativan Uses With Conditions Treated and Dose
Here’s a table outlining some common uses of Ativan (lorazepam) with the corresponding conditions treated and typical dosage ranges. You should always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical advice and dosing information:
| Use of Ativan (Lorazepam) | Conditions Treated | Typical Dosage Range |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder | 0.5 mg – 2 mg, 2-3 times per day |
| Insomnia | Short-term treatment of insomnia associated with anxiety | 1 mg before bedtime |
| Sedation | Sedation prior to medical procedures, anesthesia induction, or mechanical ventilation | 0.05 mg/kg – 0.1 mg/kg, based on weight or as directed by a healthcare provider |
| Alcohol Withdrawal | Management of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, such as agitation and tremors | 2 mg – 4 mg, 2-3 times per day or as needed |
| Status Epilepticus | Treatment of prolonged or repeated seizures | 2 mg – 4 mg, repeated at 10-15 minute intervals, up to a maximum dose of 8 mg |
| Preoperative Anxiety | Anxiety before surgical or medical procedures | 1 mg – 4 mg, 1-2 hours before the procedure |
Take control of Ativan side effects today. In case of dependence, begin your journey to recovery with We Level Up Treatment Center. Call now for a free insurance check and assessment.
How to use lorazepam?
How To Use Ativan?
Follow your doctor’s instructions when taking this medication, whether with or without food. The prescribed dosage depends on your medical condition, age, and how you respond to the treatment.
- If your doctor advises, take this medication consistently to achieve the best results. To assist with adherence, try to take it at the same time(s) every day.
- Do not discontinue using this medication suddenly without first consulting your doctor. Abruptly discontinuing the drug can exacerbate certain conditions, necessitating a gradual reduction in dosage.
- Overextended usage, this medication may lose some of its effectiveness. Discuss this with your doctor if you notice a decrease in efficacy.
- While this medication benefits many individuals, it carries a potential risk of addiction. This risk may be elevated if you have a history of substance use disorder, such as overuse or addiction to drugs or alcohol. To mitigate the risk of addiction, adhere precisely to your prescribed dosage. For additional information, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- Inform your doctor if your condition persists or worsens. Continue reading for more about the Ativan side effects and risks many encounters when taking the medication.
Overcome Ativan side effects and reclaim your life with We Level Up Treatment Center. Start your path to recovery if you’re experiencing dependence. Contact us now for a complimentary insurance check and assessment.
Ativan Side Effects
You may experience some common side effects of this medication, including drowsiness, dizziness, coordination difficulties, headaches, nausea, blurred vision, alterations in sexual interest or function, constipation, heartburn, or changes in appetite. Should any of these effects persist or worsen, promptly inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Common Ativan Side Effects
Most Common Ativan Side Effects
It’s essential to remember that your doctor has prescribed this medication because they have determined that its benefits outweigh the potential risks of side effects. Many individuals taking this medication do not experience severe side effects.
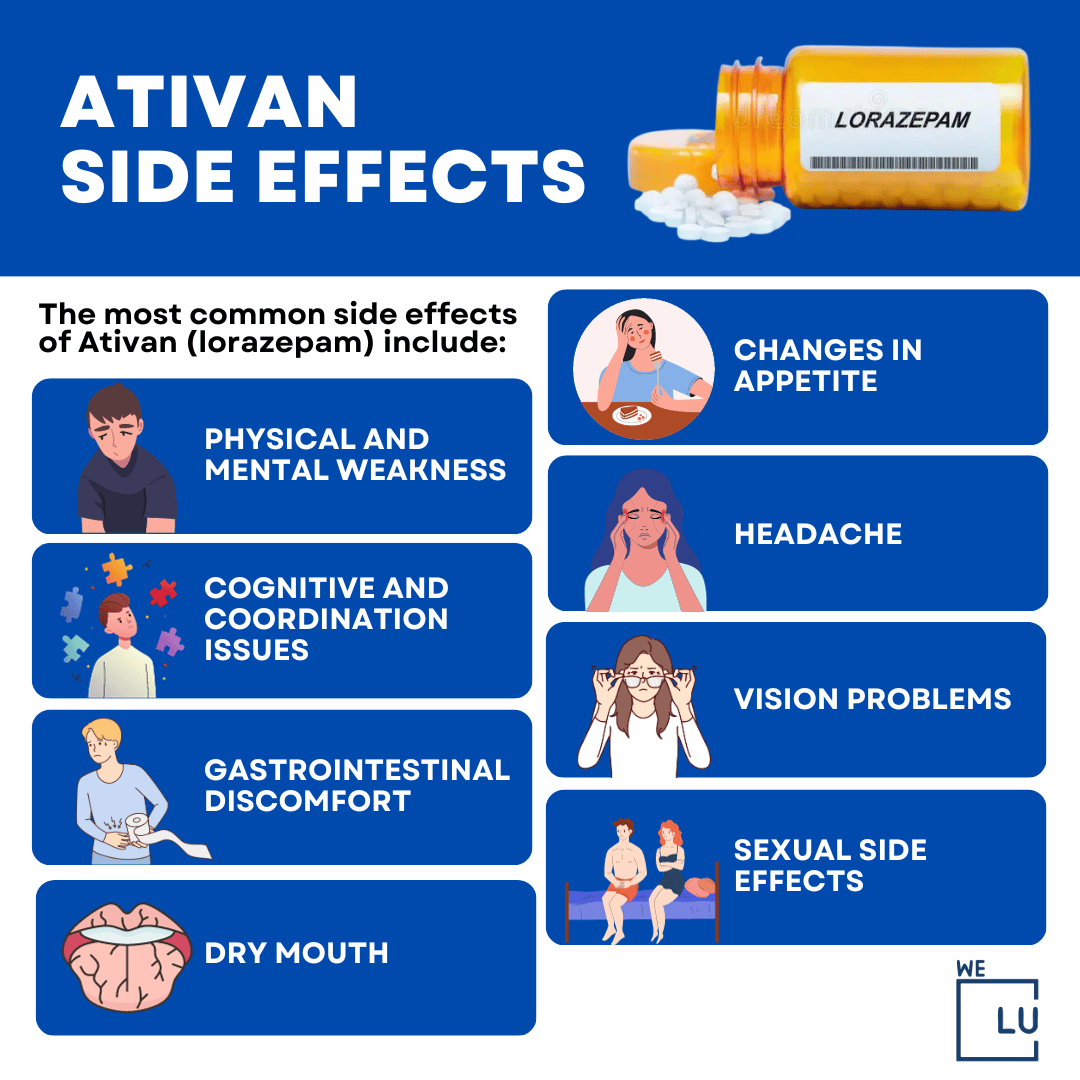
The most common side effects of Ativan (lorazepam) include:
- Drowsiness.
- Dizziness.
- Lightheadedness.
- Weakness.
- Fatigue.
- Unsteadiness.
- Slurred speech.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Memory problems.
- Constipation.
- Dry mouth.
- Headache.
- Upset stomach.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Changes in appetite.
- Vision problems.
- Sexual side effects.
These common Ativan side effects are usually mild and disappear within a few days or weeks. However, if these side effects are bothersome or do not go away, talk to your doctor. Discover additional potential Ativan side effects and risks. Keep reading to learn more.
Short-term side effects of Ativan (lorazepam) are usually mild and go away independently within a few days or weeks.
Tips to Reduce Ativan Side Effects
Here are some tips to reduce the risk of Ativan side effects:
- Start with a low dose and increase gradually as tolerated.
- Take Ativan as prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid taking Ativan with other drugs or alcohol without first talking to your doctor.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms of Ativan’s side effects, and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any.
Worried about the harmful impacts of Ativan’s side effects? We Level Up addiction experts offer a free consultation and assessment. Act now and reach out for assistance today.
Less Common Ativan Side Effects
Less common Ativan side effects
Some people may also experience less common Ativan side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions.
- Confusion.
- Hallucinations.
- Depression.
- Suicidal thoughts.
- Seizures.
- Respiratory depression.
- Coma.
If you experience these less common Ativan side effects, seek medical attention immediately. Ativan can interact with other medications, including alcohol, increasing the risk of side effects. Be sure to tell your doctor about all of the medications you are taking before starting Ativan.
Worried about the harmful Ativan side effects? Depend on We Level Up addiction experts for a complimentary consultation and evaluation. Don’t wait. Reach out for assistance now.
Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns regarding Ativan’s side effects. They can help you weigh the risks and benefits of taking this medication and can help you manage any side effects you experience.
Severe Ativan Side Effects
Severe Ativan Side Effects
Notify your doctor immediately if you encounter any severe side effects, such as mental or mood changes (such as hallucinations, depression, or thoughts of suicide), difficulty speaking, changes in vision, unusual weakness, difficulties with walking, memory issues, or signs of infection (like a persistent sore throat or fever).
If severe side effects, including yellowing of the eyes or skin, seizures, or shallow breathing, seek immediate medical attention.
In rare instances, this medication may paradoxically produce effects opposite to its usual calming properties. Signs of this contrary response may manifest as agitation, irritability, aggressive behavior, confusion, restlessness, heightened excitement, or excessive speech. If you observe any of these symptoms, promptly inform your doctor.
Severe side effects of Ativan (lorazepam) are rare but can occur. These side effects may include:
- Allergic reactions: Hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing.
- Confusion.
- Hallucinations.
- Depression.
- Suicidal thoughts.
- Seizures.
- Respiratory depression: Shallow breathing, slow breathing, difficulty breathing.
- Coma.
If you experience severe side effects, seek medical attention immediately.
Ativan can interact with other medications, including alcohol, increasing the risk of side effects. Be sure to tell your doctor about all of the medications you are taking before starting Ativan.
If you have any concerns about the side effects of Ativan, talk to your doctor. They can help you weigh the risks and benefits of taking this medication and can help you manage any side effects you experience.
Additional information:
- Ativan is a benzodiazepine medication, and benzodiazepines are known to have several potential side effects, including respiratory depression, seizures, and coma.
- Ativan is more likely to cause severe side effects in older adults, people with liver or kidney disease, and people with a history of substance abuse.
- Ativan can also be addictive, and people who take it long-term may experience withdrawal symptoms if they stop taking it suddenly.
If you are considering taking Ativan, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of this medication. While severe allergic reactions to this medication are uncommon, it is essential to seek immediate medical assistance if you experience any signs of a severe allergic reaction, which may include a rash, itching, swelling (particularly of the face, tongue, or throat), severe dizziness, or breathing difficulties.
Uncover more about potential Ativan side effects and risks. Keep reading for more.
Long-term Ativan Side Effects
Long-Term Ativan Side Effects
Long-term use of Ativan (lorazepam) can lead to some side effects, including:
- Cognitive impairment: Ativan can cause problems with memory, concentration, and attention.
- Motor impairment: Ativan can cause problems with balance, coordination, and speech.
- Addiction: Ativan is a benzodiazepine, and benzodiazepines are known to be addictive. People who take Ativan long-term may develop a physical dependence on the drug and may experience withdrawal symptoms if they stop taking it suddenly.
- Tolerance: Over time, the body can tolerate Ativan, meaning people must take higher doses to achieve the same effects. This can increase the risk of other side effects, such as overdose.
- Increased risk of falls: Ativan can cause drowsiness and dizziness, increasing the risk of falls, especially in older adults.
- Increased risk of fractures: Ativan can weaken bones, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Increased risk of pneumonia: Ativan can suppress the cough reflex, increasing the risk of pneumonia.
- Increased risk of depression: Ativan can worsen depression in some people.
- Increased risk of suicide: Ativan can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in some people.
The long-term side effects of Ativan vary from person to person. Some people may experience only mild side effects, while others may experience more severe side effects.
If you are taking Ativan long-term, talking to your doctor about this medication’s potential risks and benefits is essential. They can monitor you for any side effects and help you develop a plan to reduce your risk of side effects.
If you are concerned about the long-term side effects of Ativan, talk to your doctor about other treatment options for anxiety or insomnia.
If you are considering taking Ativan, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of this medication. While severe allergic reactions to this medication are uncommon, it is essential to seek immediate medical assistance if you experience any signs of a severe allergic reaction, which may include a rash, itching, swelling (particularly of the face, tongue, or throat), severe dizziness, or breathing difficulties.
Concerned about potential adverse Ativan side effects and dangers resulting from abuse, dependence, and withdrawal from the drug? Trust We Level Up addiction professionals to provide a free consultation and assessment. Don’t delay. Call for help today.
Find more about potential adverse Ativan side effects and dangers. Keep going for more information.
Ativan Effects on the Mind and Body
Effects of Ativan on the Mind
Discover the potential of Ativan in transforming your brain and nerves. But beware of the “rebound” side effects that may worsen your symptoms. Prepare for possible rebound anxiety, sleep disturbances, abnormal body movements, and agitation.
Experience the following side effects:
- Restlessness.
- Loss of pleasure in day-to-day experiences.
- Depression.
- Memory problems.
- Learning difficulties.
Lorazepam, the critical component of Ativan, aims to calm your brain and nerves, relieving anxiety and restlessness. However, be cautious as it may dampen your emotional responses and dull your perception. Feel a loss of interest in your everyday experiences? Constantly tired and sluggish? Look dazed and drowsy? It’s time to dig deeper into the effects of Ativan.
Ativan Effects on the Body
Experience a tranquilizing calm and physical relaxation with Ativan. This medication can relieve painful muscle spasms, prevent seizures, and slow brain and nerve activity. However, it’s essential to be aware of potential adverse reactions to this drug.
Watch out for the following possible side effects:
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Low energy levels.
- Confusion.
- Poor muscle coordination.
- Blurry vision.
- Loss of balance.
- Blood in stool or urine.
- Stomach pain.
- Weight loss.
- Chills.
- Pale, cool skin.
- Involuntary movements (tremors, shaking).
Stay cautious when using Ativan, as it can cause clumsiness, drowsiness, and disorientation. The National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration highlights that drugs in the benzodiazepine family, like Ativan, may produce symptoms similar to alcohol intoxication. This includes loss of motor coordination, slurred speech, visual disturbances, and blurred vision. If you’re planning on driving or engaging in activities that require hand-eye coordination and quick reflexes, it is essential to avoid using Ativan, especially if you’ve consumed alcohol or other sedatives. Learn more about Ativan and alcohol dangers.
Experience the benefits of Ativan, but remember to prioritize safety and stay informed about its potential risks.
Worried about the harmful Ativan side effects and the risks associated with its abuse and withdrawal? Count on We Level Up addiction experts for a complimentary consultation and evaluation. Take action now – reach out for assistance today.
Find more about potential adverse Ativan side effects and dangers. Keep going for more information.
Discover additional potential Ativan side effects and risks. Keep reading to learn more.
Ativan Warnings
Before taking lorazepam, inform your doctor or pharmacist about any allergies you may have, whether it’s an allergy to lorazepam itself, other benzodiazepines (such as alprazolam, clonazepam or diazepam), or any other substances. This product may contain inactive ingredients that could trigger allergic reactions or other complications. Consult your pharmacist for additional information.
Ativan Addiction Risks
Lorazepam carries a risk of abuse and addiction, which can result in overdose and, in severe cases, fatalities. Combining this medication with alcohol or other substances that induce drowsiness or respiratory difficulties, especially opioid medications like codeine and hydrocodone, can lead to severe side effects, including death. To mitigate these risks, your doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose of lorazepam for the shortest necessary duration. It’s crucial to understand how to take lorazepam and be aware of medications to avoid while using it; refer to the Drug Interactions section for more information. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects: slow or shallow breathing, drowsiness or dizziness, or difficulty awakening.
Ativan (Lorazepam) Precautions
Ativan Side Effects Precautions
Before commencing this medication, provide your doctor or pharmacist with your medical history, particularly if you have a history of kidney disease, liver disease, glaucoma, respiratory conditions like sleep apnea, mental or mood disorders (such as depression or psychosis), or if you have a personal or family history of substance use disorders, such as drug or alcohol overuse or addiction.
This medication can induce dizziness, drowsiness, or blurred vision. The consumption of alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) may intensify these effects. Therefore, it is advisable to refrain from driving, operating machinery, or engaging in activities that require alertness or clear vision until you can do so safely. Avoid alcohol consumption, and if you are using marijuana (cannabis), discuss it with your doctor.
Before surgery, inform your doctor or dentist about all your products, including prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal products.
Older adults may be more susceptible to the side effects of this medication, especially loss of coordination and drowsiness. These side effects can increase the risk of falls. Additionally, in older adults, lorazepam may have the opposite effect of its typical calming properties (see also Side Effects section).
In children, this medication may produce effects contrary to its typical calming properties, potentially causing restlessness, trembling, or alterations in mental and mood, such as agitation or hallucinations.
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, inform your doctor. The use of lorazepam during pregnancy is discouraged, as it can be harmful to an unborn baby. Newborns born to mothers who have used this medication late in pregnancy may exhibit symptoms like slow or shallow breathing, persistent crying, trembling, or difficulty with feeding. If you discover you are pregnant, promptly consult your doctor to discuss the risks and benefits of continuing or discontinuing this medication during pregnancy.
This drug can pass into breast milk, so it is advisable to consult your doctor before breastfeeding while using this medication. Keep reading to learn more and discover potential Ativan side effects and risks.
If you suspect intense Ativan side effects or have addiction concerns about your or someone else’s Ativan use, contact We Level Up substance abuse specialists for a comprehensive evaluation and proper support.
Ativan (Lorazepam) Addiction Symptoms
Ativan Addiction Symptoms Chart
Here’s a table outlining Ativan (lorazepam) addiction symptoms, categorized by common, less common, and rare occurrences. It also includes a severity column to indicate the potential impact of each symptom:
| Symptoms | Common | Less Common | Rare | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical dependence | ✔️ | Moderate to Severe | ||
| Withdrawal symptoms | ✔️ | Moderate to Severe | ||
| Increased tolerance | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Cravings | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Drowsiness | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Unsteady gait | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Confusion | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Memory problems | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Mood swings | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Anxiety | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Depression | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Insomnia | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Impaired coordination | ✔️ | Moderate to Severe | ||
| Respiratory depression | ✔️ | Severe | ||
| Suicidal thoughts or behaviors | ✔️ | Severe |
If you suspect severe Ativan side effects and addiction or have concerns about your or someone else’s drug use, contact a We Level Up professional addiction specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate support.
Ativan Withdrawal Risks
Ativan Withdrawal Risks
Abruptly discontinuing Ativan medication can result in severe withdrawal symptoms, potentially fatal, especially if you have been using it for an extended period or at high doses. To prevent withdrawal, your doctor may gradually reduce your dosage. Inform your doctor or pharmacist immediately if you experience withdrawal symptoms, such as headaches, sleep disturbances, restlessness, hallucinations, confusion, depression, nausea, or seizures. These withdrawal symptoms can sometimes persist for weeks to months.
Here’s a table outlining the withdrawal symptoms associated with Ativan (lorazepam) cessation, categorized by common, less common, and rare occurrences. It also includes a severity column to indicate the potential impact of each symptom:
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Common | Less Common | Rare | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Insomnia | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Irritability | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Restlessness | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Agitation | ✔️ | Moderate to Severe | ||
| Tremors | ✔️ | Moderate to Severe | ||
| Sweating | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Headaches | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Nausea and vomiting | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Loss of appetite | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Dizziness | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Confusion | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Racing thoughts | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Muscle aches | ✔️ | Mild to Moderate | ||
| Seizures | ✔️ | Severe |
Seek professional medical guidance when discontinuing Ativan or any other medication to ensure safe and appropriate withdrawal management. If you are experiencing withdrawal symptoms or are concerned about medication use, consult a We Level Up addiction specialist for personalized advice and support.
Uncover the possible Ativan side effects and their risks. Keep reading to understand more.
Ativan Interactions
Interactions between drugs can alter the effectiveness of your medications or increase the risk of severe side effects. This information does not encompass all potential drug interactions. Maintain a comprehensive list of all your products, including prescription and non-prescription medications and herbal supplements, and share this list with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not initiate, cease, or modify the dosage of any medications without your doctor’s approval.
Certain products may interact with this medication, including clozapine, kava, and sodium oxybate (gamma hydroxybutyrate or GHB).
The likelihood of experiencing severe side effects, such as slow or shallow breathing and pronounced drowsiness or dizziness, may escalate if this medication is combined with other substances that can also induce drowsiness or respiratory problems. Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are currently taking other products such as opioid pain relievers, cough suppressants (such as codeine or hydrocodone), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), other drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, diazepam, or zolpidem), muscle relaxants (such as carisoprodol or cyclobenzaprine), or antihistamines (like cetirizine or diphenhydramine).
Uncover the potential Ativan side effects and risks; keep reading to learn more.
Ativan Overdose
Call 911 in case of an Ativan overdose. Individuals exhibiting significant symptoms like fainting or difficulty breathing require medical assistance. Immediately dial a poison control hotline and get medical care.
The Dangers of an Ativan Overdose: The Signs You Need to Know
Ativan Overdose Symptoms
When used as prescribed, Ativan is generally considered safe. However, taking too much of this medication can lead to an overdose, which can have severe consequences, including coma or even death. Shockingly, the number of overdose-related deaths associated with prescription benzodiazepines like Ativan has quadrupled since 2001.
As a central nervous system depressant, Ativan slows down brain and nerve activity. In regular doses, it rarely causes unconsciousness or death. But when taken in excessive amounts, particularly when combined with other drugs that suppress the brain’s functions, Ativan can be deadly. Many cases of overdose, whether accidental or intentional, have been linked to the use of Ativan with alcohol, certain pain medications, other anti-anxiety drugs, and sleep aids.
Being able to identify the signs of a lorazepam overdose is crucial, as it can mean the difference between life and death:
- Pale, cool, bluish skin or lips.
- Shallow, slow breathing.
- Excessive sedation or drowsiness.
- Difficulty walking and loss of coordination.
- Slurred speech.
- Memory problems.
- Confusion.
- Weakness.
- Loss of consciousness.
An Ativan overdose is a medical emergency; immediate attention is essential to prevent a fatal outcome. It is crucial never to leave someone overdosed on Ativan alone, especially if other drugs are involved.
Remember, recognizing the signs and acting quickly can save lives.
Discover the potential hazards and Ativan side effects that you might encounter. Continue for more.
Overdose Symptoms of Ativan
Ativan Overdose Symptoms
Ativan (lorazepam) is a benzodiazepine medication commonly prescribed for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. It is a powerful sedative and can be dangerous in high doses.
An Ativan overdose can occur when someone takes more medication than prescribed or combines it with other drugs or alcohol. Symptoms of an Ativan overdose can include:
- Drowsiness.
- Confusion.
- Slurred speech.
- Impaired coordination.
- Shallow breathing.
- Slow heart rate.
- Low blood pressure.
- Coma.
In severe cases, an Ativan overdose can be fatal.
If you suspect someone has overdosed on Ativan, it is vital to call 911 immediately. Until help arrives, you can try to keep the person awake and alert. You can give them artificial respiration if they are breathing slowly or shallowly.
There is no specific antidote for an Ativan overdose, but treatment typically involves supportive care, such as providing oxygen and fluids. In some cases, medications may be used to reverse the effects of the overdose.
If you are taking Ativan, following your doctor’s instructions carefully and avoiding taking more than prescribed is essential. It is also important to avoid taking Ativan with other drugs or alcohol, as this can increase the risk of an overdose.
Here are some tips to prevent an Ativan overdose:
- Take Ativan exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do not take more Ativan than prescribed.
- Do not take Ativan with other drugs or alcohol.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms of an Ativan overdose.
- If you suspect that someone has overdosed on Ativan, call 911 immediately.
Discover the potential risks and Ativan side effects that countless individuals might experience. Continue on for more.
What to do in case of Ativan overdose?
What to do for an Ativan overdose?
If you suspect an Ativan overdose, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately. Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
While you are waiting for help to arrive, there are a few things you can do to help the person:
- Stay with the person and monitor their breathing and pulse.
- If the person is unconscious, place them in the recovery position on their side.
- If the person is vomiting, turn them on their side to prevent choking.
- Do not give the person any food or drink.
- Tell the medical personnel what kind of Ativan the person took and how much.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind:
- Do not try to make the person vomit.
- Do not give the person any other medications.
- Do not leave the person alone.
Overdose is a medical emergency, and it is vital to seek medical attention immediately. Discover the potential Ativan side effects and overdose risks you need to know. Keep reading to stay informed.
Ativan Overdose Treatment
Treatment for an Ativan Overdose
Treatment for an Ativan overdose depends on the severity of the overdose and the presence of any other medical conditions. If the overdose is mild, the patient may be monitored in the emergency department until they become more alert and their vital signs are stable. If the overdose is more severe, the patient may need to be admitted to the hospital for further observation and treatment.
There is no specific antidote for Ativan overdose, but several medications can be used to treat the symptoms. For example, flumazenil can be used to reverse the sedative effects of Ativan, but it should be used with caution as it can also induce seizures. Other medications that may be used in the treatment of an Ativan overdose include:
- Activated charcoal to absorb any remaining Ativan in the stomach.
- Intravenous fluids to maintain hydration and blood pressure.
- Mechanical ventilation to support respiration.
If the patient has a history of seizures, they may be given anticonvulsant medications to prevent seizures from occurring.
In severe cases of Ativan overdose, the patient may need to be placed on a ventilator to support their breathing. They may also need to be intubated to protect their airway.
The goal of treatment for an Ativan overdose is to stabilize the patient’s vital signs and to support their breathing until the effects of the drug have worn off. Most people who overdose on Ativan make a full recovery.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about Ativan overdose treatment:
- You must seek medical attention immediately if you suspect an Ativan overdose.
- Treatment for an Ativan overdose may involve multiple medications, including flumazenil, activated charcoal, intravenous fluids, mechanical ventilation, and anticonvulsant medications.
- The goal of treatment is to stabilize the patient’s vital signs and to support their breathing until the effects of the drug have worn off.
- Most people who overdose on Ativan make a full recovery.
Discover the potential risks and Ativan side effects of the drug’s misuse. Keep reading to learn more.
Learn about the potential Ativan side effects and risks; continue to read to learn more.
Ativan Imprint
Here’s a table providing information about Ativan, including its typical dose, condition for use, color, shape, and imprint:
| Ativan | Typical Dose | Color | Shape | Imprint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ativan 0.5mg | 0.5mg | White | Five-Sided | A BPI 63 |
| Ativan 1mg | 1mg | White | Five-Sided | A BPI 64 |
| Ativan 2mg | 2mg | White | Five-Sided | A 2 BPI 65 |
Discover the potential Ativan side effects and risks when using this medication. Keep reading to learn more.
Ativan Abuse: The Risks Are Real
Ativan, also known as lorazepam, is a widely prescribed medication in the United States for treating anxiety, insomnia, and other related conditions. While Ativan has many benefits for those suffering from these conditions, it can quickly become addictive and cause severe side effects if abused or taken for prolonged periods.
The dangers of Ativan abuse, dependence, and withdrawal are often underestimated or ignored by individuals prescribed the drug. However, if you or someone you know struggles with Ativan addiction, you don’t have to face it alone. We Level Up addiction professionals offer a free consultation and assessment to help you or your loved one overcome addiction. We’ll look closer at common Ativan side effects, abuse, and dependence risks and guide you in seeking help.
Regain control over Ativan side effects today. If you’re experiencing dependency, embark on your path to recovery with We Level Up NJ. Contact us now for a complimentary insurance check and assessment.
Most Common Ativan Side Effects
The more common Ativan side effects include:
- Drowsiness or sleepiness.
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
Some people may also experience less frequent Ativan side effects, such as:
- Confusion.
- Lack of coordination.
- Depression.
- Fatigue.
- Headache.
- Restlessness.
- Changes in libido (sex drive).
- Memory problems.
In people who receive the Ativan injection, redness or deepening of skin color and pain at the injection site can commonly occur.
Some of these side effects may disappear within a few days or weeks. Talk with your doctor or pharmacist if they’re more severe or don’t go away.
Serious Ativan Side Effects
Serious side effects from Ativan aren’t typical, but they can occur. Call your doctor right away if you have any severe Ativan side effects. Call 911 if your symptoms feel life-threatening or if you think you have a medical emergency.
Severe Ativan side effects and symptoms can include the following:
- Slowed breathing.
- Respiratory failure, which is rare.
- Low blood pressure may be severe enough to cause fainting or falls.
- Convulsions or seizures.
- Uncontrollable, sudden movements in your arms or legs.
- Loss of consciousness or awareness.
- Stiff muscles.
- Staring spells.
- Paradoxical reactions (reactions that cause effects opposite to those expected with the drug), such as aggression, hostility, agitation, or rage.
- Dependence, misuse, and addiction are more likely in people who take higher doses of Ativan or use it long-term or those who misuse alcohol or drugs.
What is Ativan?
Ativan (lorazepam) is a prescription tranquilizing drug. You might also know it as a sedative-hypnotic or anxiolytic medication. Ativan is used for anxiety treatment [1]. It is in a class of medications called benzodiazepines. It works by slowing activity in the brain to allow for relaxation. Many have succumbed to Ativan addiction, requiring Ativan detox to function normally again and avoid Ativan side effects that bring health risks.
Ativan is the brand name available in the US for lorazepam. Loraz, another brand name for lorazepam, has been terminated in the US. Ativan is obtainable in generic form; however, you need a prescription from your doctor. Despite its legitimate medical uses, Ativan has known addictive and drug dependence liabilities.
This is one of the reasons why Ativan is prescribed for relatively short-term use. However, people should be careful to adhere to prescription guidelines. If not, if an individual exceeds the recommended dosage, it may increase the likelihood of drug addiction development.
Ativan is a DEA-controlled drug. The active ingredient, Lorazepam, is a DEA Schedule IV controlled substance. Given that, substances in the DEA Schedule IV have a low potential for abuse relative to substances in Schedule III. The DEA also classifies Ativan as a Depressant. Moreover, the street names for Benzodiazepines, including Ativan, are Benzos, Downers, Nerve Pills, and Tranks. [2]
Ativan and Alcohol Dangers
Combining Ativan with alcohol can be incredibly dangerous, even life-threatening. The long-term effects of using these two substances together can damage your health and even lead to death.
Ativan and alcohol are depressants that can slow down the central nervous system in your body. When used together, the effects of both substances are intensified, making it incredibly dangerous. Ativan enhances the effects of alcohol, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, difficulty breathing, coma, and even death.
We’ll explore the dangers of Ativan side effects, including when mixed with alcohol. Learn the risks to your health.
Ativan Side Effects Can Be Dangerous
Ativan (lorazepam) side effects can include declining mental alertness, which may decrease overall performance and an increased risk of accidental injury. Patients may also experience drowsiness, fatigue, headache, blurred vision, and dry mouth. Ativan (lorazepam) should not be used in patients with a known sensitivity or allergy to the drug, as this can cause anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
Skip To:
Learn More:
- Anxiety Treatment
- Ativan Addiction Treatment
- Ativan Detox
- Ativan and Alcohol
- Ativan vs Valium, What’s the Difference and Which is Better? Ativan to Valium Conversion. Is Valium Stronger than Ativan?
- Understanding Ativan Withdrawal Symptoms, Ativan Withdrawal Timeline, and Treatment. Ativan For Alcohol Withdrawal.
- Is Ativan Stronger Than Klonopin? Ativan vs Klonopin, Differences and Side-Effects. Switching From Ativan to Klonopin.
- How Does Ativan Make You Feel? Ativan Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, & Risks. Ativan Dose. Ativan High. Ativan Abuse & Addiction Treatment.
- Ativan Vs Xanax Differences Vs Similarities. Which is Stronger & More Effective. Xanax vs Ativan Drug Facts.
- How Long Does Ativan Last?
- Signs of Drug Addiction
- Dual Diagnosis Link to Addiction, Deadly Risks, Signs, Statistics, & Treatment Options.
- Detox Rehab
Experience Ativan side effects? Struggling with misuse or dependence? Reach out to the We Level Up NJ addiction specialists for help. Discover solutions to your questions about risks and withdrawal. Schedule a free assessment now, available 24/7.
Top 20 Most Frequently Asked Questions About Ativan Side Effects
What are the side effects of Ativan?
Ativan (lorazepam), a medication commonly prescribed for anxiety and insomnia, can cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion. In some cases, it may also lead to more severe side effects like memory problems, addiction, or allergic reactions, so it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional and as prescribed.
How long does Ativan last?
The duration of action for Ativan (lorazepam) typically ranges from 6 to 8 hours. However, individual factors such as metabolism and dosage can influence how long the effects of the medication last in a person’s system.
How long does Ativan stay in your system?
Ativan (lorazepam) can generally be detected in standard urine tests about 2 to 6 days after the last dose. However, the duration it stays in an individual’s system can vary based on factors like metabolism and the frequency of use.
Does Ativan cause weight gain?
Weight gain is not a common side effect of Ativan (lorazepam). However, some individuals may experience changes in appetite or weight due to reduced anxiety or improved sleep while taking the medication, but this is not a direct effect of Ativan itself. If you have concerns about weight changes while using Ativan, discussing them with your healthcare provider is essential.
Does Ativan lower heart rate?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can lower heart rate as one of its potential side effects. It is considered a central nervous system depressant, and it can slow down various bodily functions, including heart rate and breathing, especially when taken in higher doses or in combination with other substances that depress the central nervous system. If you experience a significant decrease in heart rate while taking Ativan, seeking medical attention is necessary.
Will Ativan lower blood pressure?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can lower blood pressure as it is a central nervous system depressant. It can relax blood vessels and reduce overall cardiovascular activity, potentially leading to a decrease in blood pressure, especially at higher doses or when combined with other medications that also lower blood pressure. If you have concerns about Ativan affecting your blood pressure, Discuss this with your healthcare provider, as they can monitor and adjust your treatment as needed.
Does Ativan speed up death?
Ativan (lorazepam) is not intended or prescribed to speed up death. It is primarily used in medical practice to manage anxiety, insomnia, and certain medical conditions. Any use of medications for purposes other than their intended medical indications should be approached with extreme caution and only under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Do Ativan make you sleepy?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) is known for its soothing properties, and it commonly causes drowsiness and sleepiness as a side effect. This soothing effect is often why it is prescribed for conditions like anxiety and insomnia. Still, it can also impair alertness, so it’s essential to use it as directed by a healthcare provider and avoid activities that require full attention, such as driving while taking it.
Can Ativan cause hallucinations?how long does it take for ativan to wear off
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can sometimes lead to hallucinations as a side effect. Hallucinations are more likely to occur when the medication is misused, taken in higher doses, or when an individual is predisposed to such impacts. If you or someone you know experiences hallucinations while taking Ativan, seek medical attention promptly.
How does Ativan make you feel the next day?
The way Ativan (lorazepam) makes you feel the next day can vary from person to person. While some individuals may feel residual drowsiness or grogginess, others may not experience any lingering effects. Be cautious when taking Ativan, especially before engaging in activities requiring alertness, and follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding its use to minimize any potential aftereffects.
How long does it take for Ativan to wear off?
The effects of Ativan (lorazepam) typically start to wear off within a few hours, with the peak effects occurring about 2 to 4 hours after taking the medication. However, the duration may vary depending on the individual’s metabolism and dose.
Is Ativan addicting?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can be addicting, mainly if misused, for extended periods, or at higher doses than prescribed. It belongs to the benzodiazepine class of drugs with potential physical and psychological dependence. Use it only as directed by a healthcare provider to minimize the risk of addiction.
Is Ativan a controlled substance?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) is classified as a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States. It is categorized as a Schedule IV controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and dependence.
Is Ativan an opioid?
No, Ativan (lorazepam) is not an opioid. It is a medication from the benzodiazepine class that treats anxiety, insomnia, and certain medical conditions by affecting the central nervous system differently than opioids. Opioids, on the other hand, are a separate class of drugs primarily used for pain management and act on opioid receptors in the brain and body.
Can you overdose on Ativan?
Yes, it is possible to overdose on Ativan (lorazepam) if taken excessively or combined with other substances that depress the central nervous system, such as alcohol or opioids. An overdose can lead to severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, and even death. Use Ativan only as a healthcare provider prescribes and seek immediate medical attention if an overdose is suspected.
Can you take Ativan while pregnant?
The use of Ativan (lorazepam) during pregnancy should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare provider. It is generally recommended to avoid benzodiazepines like Ativan during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, as they can potentially pose risks to the developing fetus. However, in some cases, when the benefits of using Ativan outweigh the potential risks, a healthcare provider may prescribe it for a pregnant individual. Still, the dose and duration will typically be kept as low as possible. Pregnant individuals must thoroughly discuss with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision regarding the use of Ativan during pregnancy.
Is Xanax stronger than Ativan?
Xanax (alprazolam) and Ativan (lorazepam) are both benzodiazepines and have similar potency. However, the strength of their effects can vary from person to person, and one may be perceived as more potent than the other based on individual reactions. Both medications should be used as prescribed by a healthcare provider, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and response of the patient.
Is Ativan stronger than Klonopin?
Ativan (lorazepam) and Klonopin (clonazepam) are both benzodiazepines, and their relative strength can vary from person to person. Generally, the potency of these medications is similar, and the choice between them depends on individual factors and the specific medical condition being treated. Both should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, and the dosage should be determined based on the patient’s needs and response.
How long after drinking can I take Ativan?
It’s generally advisable to avoid taking Ativan (lorazepam) shortly after drinking alcohol because both substances can depress the central nervous system. Combining them can lead to increased sedation, impaired coordination, and potentially dangerous side effects. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for specific guidance on when it may be safe to take Ativan after consuming alcohol, as the timing can depend on various factors, including the amount of alcohol consumed and an individual’s tolerance. In many cases, it’s best to avoid the combination altogether to ensure safety.
How long does Ativan take to work?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically starts to work relatively quickly, with its effects becoming noticeable within 15 to 30 minutes after taking it orally. However, the exact onset of action can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s metabolism and the treatment condition.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug & Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You? Or Mental Health Support?
Even if you have failed previously, relapsed, or are in a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. Call us when you feel ready or want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7Ativan Side Effects and Ativan Withdrawal Dangers
Ativan, like many other benzodiazepines, can be highly addictive, even when taken as directed by a physician. The drug enhances the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA, which produces a calming and sedative effect, making it an effective treatment for anxiety. However, if Ativan is abused or taken for a prolonged period, the brain becomes dependent on the drug’s calming effects to function normally. If a person tries to stop taking the medication suddenly, it can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, hallucinations, and delirium tremens.
Overcoming Ativan Addiction: Recognize the Signs and Find Treatment.
Find yourself relying on Ativan a little too much? You may be dealing with an addiction. Ativan addiction is most common among those who overuse the medication, use it recreationally, or combine it with other sedatives. But don’t worry, there is hope for recovery.
Ativan Abuse Side Effects
Ativan Addiction Deepens Ativan Side Effects
Ativan can cause several adverse side effects when abused, ranging from mild to severe. These side effects include drowsiness, memory impairment, decreased concentration, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. When combined with alcohol or other substances, Ativan’s effects can be even more dangerous.
Furthermore, Ativan abuse can have long-lasting negative consequences on a person’s life, including job loss, financial instability, and relationship breakdown.
At the same time, it can be challenging to recognize the signs that someone is addicted to Ativan, especially since many people who abuse the drug may not know the severity of their dependence. Some common signs of Ativan addiction include taking more of the medication than prescribed, difficulty stopping or reducing the use of the drug, and experiencing withdrawal symptoms when the medication is stopped.
If you or someone you love is struggling with Ativan addiction, it’s crucial to seek professional help from addiction professionals like We Level Up. Our addiction professionals take a comprehensive approach to treatment and recovery, providing personalized care and support for every individual’s unique needs. This includes medical detoxification, behavioral therapy, and counseling to address underlying mental health issues that may be contributing to addiction. Most importantly, we believe in treating the whole person, not just the symptoms of addiction.
Regain control from Ativan side effects. Start your journey to recovery today at We Level Up Treatment Center. Contact us now for a complimentary insurance check and assessment.
Ativan Withdrawal Side Effects
Ativan Withdrawal
After taking Ativan for a few weeks, your body becomes accustomed to its effects. This can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses to feel the same relief. If you misuse Ativan, tolerance can spiral into addiction, leading to Ativan withdrawal, accompanied by an uncontrollable urge to seek and use the drug.
So, what are the signs of Ativan withdrawal and addiction? Restlessness, obsession with getting more of the drug, loss of control over dosage, isolating yourself, decline in work or school performance, and a decline in physical appearance are all red flags. Additionally, withdrawal symptoms like seizures, agitation, and hallucinations can occur when stopping the drug.
But there is a way out. A gradual drug taper, supervised by a We Level Up Ativan detox specailists, can minimize withdrawal symptoms and help you safely stop using Ativan. Alongside this, We Level Up’s Ativan treatment for addiction and access to peer support can rebuild your life.
Don’t let Ativan side effects control you. Take the first step towards recovery today with We Level Up Treatment Center. Call for a free insurance check and assessment.
Ativan can be a lifesaver for those struggling with anxiety and related conditions. However, the risks of abuse and dependence cannot be ignored or underestimated. If you or someone you know is struggling with Ativan addiction, don’t wait. Seek help from addiction professionals like We Level Up NJ, who understand the complexity of addiction and can provide the necessary treatment and support for recovery. With the right help and guidance, overcoming addiction and leading a healthy, fulfilling life is possible.
Ativan Drug Fact Sheet
Ativan Uses
This drug is prescribed to relieve anxiety. Lorazepam belongs to a class of drugs known as benzodiazepines, which act on the brain and nerves (central nervous system) to have a calming effect. Ativan boosts the effects of a specific natural molecule in the body. Ativan side effects should be discussed with your doctor before using the drug.
How To Use Ativan?
As prescribed by your doctor, take this medication by mouth with or without food. Your age, health status, and treatment response determine the dosage.
- Use this medication as prescribed by your doctor to get the most benefit from it. Use it at the same time(s) every day to help you remember.
- Although Ativan may benefit patients, this medication occasionally leads to addiction. If you have a substance use disorder, such as excessive or compulsive drug or alcohol use, your risk may be higher. To lessen the possibility of addiction, take this medication exactly as directed. To learn more, consult your physician or pharmacist.
- Do not abruptly stop taking this medication without first talking to your doctor. When this medication is abruptly stopped, certain conditions could get worse. It might be necessary to reduce your dosage gradually.
- Long-term use of this medication may cause it to lose some of its effectiveness. If this medication stops working as well, consult your doctor.
- Tell your doctor if your condition persists or worsens or you feel Ativan’s side effects.
Ativan 1mg Side Effects
The most common side effects of Ativan 1mg include sleepiness, dizziness, light-headedness, confusion, headache, blurred vision, trembling, sweating, and nausea. Other more severe side effects can include chest pain, trouble breathing, irregular heartbeat, and changes in behavior. If you experience any of these side effects, it is essential to stop taking Ativan and consult your doctor right away.
Ativan 1mg side effects can also include depression, anxiety, irritability, difficulty concentrating and memory. It may increase the risk of developing specific mental severe health problems. In some cases, Ativan 1mg side effects have been associated with an increased risk of seizures. Long-term Ativan 1mg side effects include a risk of physical dependence, which can cause withdrawal symptoms if stopped suddenly. Seek medical help if you or someone you know struggles with Ativan abuse or addiction.
Ativan Side Effects in Elderly
Possible side effects of taking Ativan in elderly people include confusion, unsteadiness, falling, constipation, dry mouth, and headache. Additionally, Ativan can increase the risk of depression or worsen existing depression. It’s important to discuss with your doctor any potential risks or side effects of taking Ativan.
Ativan side effects have also been linked to an increased risk of memory problems and cognitive decline in the elderly. It can also cause low blood pressure and dizziness, leading to a fall risk. It may also interfere with the metabolism of medications, resulting in potentially dangerous interactions. As with any medication, having regular conversations with your doctor and monitoring any side effects is essential.
Ativan Side Effects Precautions
Inform your doctor or pharmacist before taking lorazepam if you have any allergies, other benzodiazepines (like alprazolam, clonazepam, or diazepam), or other substances. Inactive ingredients in this product can potentially trigger allergic reactions or other issues. To learn more, speak with your pharmacist about Ativan’s side effects.
Inform your doctor or pharmacist about your medical history before taking this medication, mainly if it includes any of the following conditions: kidney disease, liver disease, glaucoma, lung/breathing issues (such as sleep apnea), mental/mood disorders (such as depression, psychosis), or a personal or family history of a substance use disorder (such as excessive or addiction to drugs or alcohol).
This drug may cause you to feel groggy, sleepy, or have blurred vision. You may become more woozy or sleepy after consuming alcohol or marijuana (cannabis). Until you can do something safely, avoid operating machinery, driving, or anything else requiring alertness or sharp vision. Avoid drinking alcohol. Consult your physician if you use marijuana (cannabis). Inform your surgeon or dentist of all the products you use before surgery (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).


Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care at the We Level Up Treatment Centers Network.
Hotline (877) 378-4154Ativan Side Effects and Addiction Statistics
Ativan is primarily prescribed to treat anxiety, panic attacks, insomnia, seizures, and alcohol withdrawal. However, when misused, Ativan can quickly become addictive. Long-term side effects of Ativan abuse include memory problems, impaired thinking, and decreased motor coordination. Additionally, withdrawal from Ativan can be severe and uncomfortable. Treatment for Ativan addiction often includes a combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy, medications, and other forms of therapy and support.
The national statistics are never a complete picture of addiction rates. You should know that according to statistics on Ativan addiction, benzodiazepine use is consistently high. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, less than 1% of people aged 12 and older misused prescription benzodiazepines like Ativan in the past month. Additionally, the non-medical use of benzodiazepines has been declining since the early 2000s.
27 million
With more than 27 million prescriptions written as of 2011, Ativan ranked fifth among the most frequently prescribed benzodiazepines (and the number has continued to rise).
Source: NIH
75%
Approximately 75% of people who sought medical attention for benzodiazepine overdoses also abused opioid painkillers, usually for fun.
Source: NIH
20%
An extended hospital stay or death occurs in about 20% of all emergency room visits for benzodiazepine-related distress.
Source: NIH
Long-Term Side Effects of Ativan
Long-term side effects of Ativan can include cognitive decline, memory deficits, confusion, loss of coordination, and slowed reflexes. The long-term side effects of Ativan may include increasing the risk of developing a seizure disorder and increasing the risk of anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, long-term use of Ativan may lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms if stopped suddenly.
Moreover, when taking Ativan long-term, working closely with your healthcare provider to monitor any possible Ativan side effects is essential. You should also take the medication as directed to avoid any possible complications. It’s important to talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you are concerned about any Ativan side effects that you may experience. You should not start or stop taking Ativan without first talking to your doctor.
Ativan Side Effects in Children
In children, Ativan side effects may have the opposite of its typical calming effect, resulting in restlessness, shaking, or changes in mental state (such as agitation and hallucinations).
The most common side effect of Ativan in children is drowsiness, which varies depending on the child’s age and dosage. Other potential side effects may include headaches, nausea, irritability, aggression, confusion, restlessness, impulsiveness, and difficulty sleeping. Rarely, more severe side effects such as seizures, hallucinations, vision changes, and chest pain may occur. It is important to watch children closely for any side effects and to contact your doctor if you notice any signs of adverse reactions.
Side Effects for Ativan During Pregnancy
Ativan should not be taken during pregnancy unless necessary, as some studies suggest it may increase the risk of birth defects and other complications. Taking Ativan while pregnant could also increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, or neonatal withdrawal syndrome, leading to developmental problems in the baby.
Let your doctor know if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant. Lorazepam usage should not be combined with pregnancy. Consult your doctor as soon as possible about the risks and advantages of this medication if you find out you’re pregnant. An unborn child could suffer harm from lorazepam. Call the doctor immediately if you observe symptoms in your newborn baby, such as slowed breathing, feeding issues, or persistent crying. For further information, talk to your doctor.
Ativan Side Effects for Breast Feeding
It is not recommended to take Ativan while breastfeeding due to the potential adverse side effects it could have on the baby. However, if you and your doctor feel the medication’s benefits outweigh the risks, taking small doses for short periods may be considered safe. Monitor your baby for any signs of adverse reactions, such as excessive sleepiness, difficulty feeding, or irritability. This medication enters breast milk. Before breastfeeding, speak with your doctor.
How Long Do The Effects Of Ativan Last?
How long do the effects of Ativan last? The amount of time Ativan lasts will depend on how much you take and your own body, but generally, Ativan lasts about six to eight hours. It should start working about 20-50 minutes after you take it, and you’ll feel the effects of Ativan most strongly about two hours after taking it.
The Ativan half-life is about 12 hours, which means about half of the Ativan you took will still be in your body at that point. But how long does Ativan last in your system? For most people, Ativan will be out of their system within three days. However, if you’ve been on this medication for a long time, such as a few months or more, and developed a high tolerance, Ativan can remain detectable several weeks after taking it.
Ativan Effects On The Body
Ativan also affects physical functions and responses by slowing the brain’s and nerves’ activity. As a tranquilizer, Ativan can make the user feel calm and physically relaxed. When taken correctly, Ativan can also stop painful muscle spasms or prevent life-threatening seizures. This medication is generally safe and effective for patients who take Ativan as directed for legitimate reasons. However, all users must watch out for potential adverse reactions to the drug, such as:
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Low energy levels.
- Confusion.
- Poor muscle coordination.
- Blurry vision.
- Loss of balance.
- Blood in stool or urine.
- Stomach pain.
- Weight loss.
- Chills.
- Pale, cool skin.
- Involuntary movements (tremors, shaking).
Since it can cause clumsiness, drowsiness, and disorientation, Ativan increases the risk of accidental injuries. The National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration cautions that drugs in the benzodiazepine family, like Ativan, can cause symptoms that resemble alcohol intoxication, such as loss of motor coordination, slurred speech, visual disturbances, and blurred vision. Driving under the influence of Ativan or performing other activities that require hand-eye coordination and quick reflexes can be extremely dangerous, especially if the user has also consumed alcohol or other sedatives.
Ativan Effects On The Mind
Ativan can have powerful effects on the brain and nerves. However, many users experience “rebound” side effects or worsen the same symptoms that the drug is designed to treat. In particular, Ativan can cause rebound anxiety, sleep disturbances, abnormal body movements, and agitation. Other side effects can include:
- Rebound anxiety.
- Restlessness.
- Loss of pleasure in day-to-day experiences.
- Depression.
- Memory problem.
- Learning difficulties.
The chemical structure of lorazepam is intended to reduce the brain’s and nerves’ excitability while soothing emotional responses that create anxiety and restlessness. On the negative side, Ativan can flatten users’ emotional responses and blunt their experiences of the world. As a result, individuals taking Ativan may lose interest in their everyday experiences or responsibilities. As a result, they may feel constantly sluggish and tired and have a dazed, exhausted appearance.
Do you have questions about the Ativan side effects or treatment in general? Call our helpline 24/7.
Top 20 What Does Ativan Feel Like? Ativan Side Effects FAQs
How long does Ativan work?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically starts working within 30 minutes to 1 hour after taking it, and its effects can last anywhere from 6 to 8 hours. However, the duration of action can vary from person to person. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for dosing and timing to avoid Ativan side effects.
How much Ativan is too much?
The appropriate dosage of Ativan (lorazepam) varies depending on an individual’s medical condition and the doctor’s recommendations. Taking too much can lead to severe Ativan side effects, including overdose symptoms such as extreme drowsiness, confusion, slowed or shallow breathing, and even coma. Take Ativan as a healthcare professional prescribes and not exceed the recommended dosage to avoid potential overdose risks. If you suspect an overdose, seek immediate medical attention.
Which is stronger Ativan or Xanax?
Both Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam) are benzodiazepine medications used to treat anxiety and panic disorders, but their strength can vary from person to person. In general, Xanax is often considered more potent and fast-acting than Ativan, which may make it more robust regarding immediate anxiety relief. Still, it also has a higher potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms when used long-term. The choice between the two should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering an individual’s needs and medical history.
Does Ativan make you feel happy?
Ativan (lorazepam) is primarily prescribed as an anti-anxiety and sedative medication. While it can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm, it is not typically used to induce happiness or euphoria. Its effects are more focused on alleviating stress and promoting relaxation rather than generating feelings of happiness.
How long is Ativan in your system?
The half-life of Ativan (lorazepam) is typically around 10 to 12 hours. It can take several half-lives for a drug to be mostly eliminated from the body so that it may remain detectable in urine or blood tests for a few days to a week after the last dose. Still, the exact duration can vary among individuals.
Does Ativan help with nausea?
Ativan (lorazepam) may help with nausea in certain situations, primarily when nausea is related to anxiety or anticipatory nausea before a medical procedure. It has a calming effect that can reduce anxiety-induced nausea, but it is not typically used as a primary treatment for nausea unrelated to anxiety or specific medical conditions. Other medications like antiemetics may be more effective for nausea due to other causes, such as motion sickness or chemotherapy-induced nausea.
How long does 1mg Ativan last?
The effects of a 1mg dose of Ativan (lorazepam) typically last around 6 to 8 hours. However, the duration can vary from person to person based on factors such as individual metabolism and tolerance, so it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding dosing frequency.
Does Ativan help with pain?
Ativan (lorazepam) is not primarily used as a pain medication. It is a benzodiazepine for anxiety, insomnia, and certain seizure disorders. While it may have a mild sedative effect that can help some individuals feel more comfortable, it is not a recommended treatment for managing pain. Pain management typically involves using specific pain relievers or analgesics prescribed by a healthcare provider.
How long does it take Ativan to lower blood pressure?
Ativan (lorazepam) is not typically used to lower blood pressure. Its primary use is for anxiety and related conditions. If you have concerns about your blood pressure and Ativan side effects, consult a healthcare professional who can recommend appropriate treatments or medications designed explicitly for managing blood pressure.
What is the difference between Ativan and Xanax?
Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam) are both benzodiazepines used to treat anxiety and panic disorders, but they have some differences. One key difference is their duration of action, with Xanax having a faster onset and a shorter time, making it more suitable for acute anxiety or panic attacks. In contrast, Ativan has a longer duration and may be preferred for generalized anxiety disorder. Moreover, individual responses to these medications can vary, so the choice between them should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider based on the patient’s needs and medical history.
How long does Ativan stay in urine?
Ativan (lorazepam) in urine can typically be detected up to 3 to 6 days after the last dose. However, this can vary depending on factors such as an individual’s metabolism and the sensitivity of the drug test. It’s important to note that drug detection times can vary, so if you have concerns about a drug test, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider or the organization conducting the test for more precise information.
How to get Ativan prescribed?
To get Ativan (lorazepam) or any prescription medication, you should schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider, such as a doctor or psychiatrist. During the meeting, discuss your symptoms and medical history honestly. If the healthcare provider determines that Ativan is an appropriate treatment for your condition, they can write you a prescription. Use prescription medications only as a healthcare professional directs, and do not seek them without a legitimate medical need.
What is a good natural substitute for Ativan?
Several natural approaches may help alleviate anxiety and stress without medication like Ativan. These include mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep. Additionally, herbal remedies like valerian root, passionflower, and chamomile have traditionally been used to promote relaxation and may offer a natural alternative. Consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment for anxiety.
When does Ativan peak?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically reaches its peak concentration in the bloodstream within 1 to 2 hours after oral ingestion. This peak concentration corresponds to when the medication’s effects, such as anxiety reduction and sedation, are most pronounced.
When to give Ativan for seizure?
Ativan (lorazepam) is often used to treat acute seizures. It is typically administered when a seizure begins or as soon as possible after a seizure starts to help stop or control the seizure activity. A healthcare professional, such as a doctor or paramedic, should determine the specific timing and dosage based on the individual’s medical history and the circumstances surrounding the seizure.
Can you take Klonopin and Ativan in the same day?
Taking Klonopin (clonazepam) and Ativan (lorazepam) together on the same day is generally not recommended unless specifically instructed by a healthcare provider. Both medications belong to the same class of drugs (benzodiazepines), and combining them can increase the risk of side effects and excessive sedation. Follow your doctor’s advice and not self-administer multiple benzodiazepines simultaneously.
How long does .5 Ativan last?
A 0.5mg dose of Ativan (lorazepam) typically has a duration of action of around 6 to 8 hours. However, individual responses to the medication can vary, so the exact time of effect may differ from person to person. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding dosing frequency and not exceed the prescribed dosage.
How long does IV Ativan last?
The duration of IV (intravenous) Ativan (lorazepam) can vary depending on factors such as the dosage administered and the individual’s response. In general, the effects of IV Ativan can be relatively rapid, typically within a few minutes, and may last for several hours, with peak effects occurring sooner than oral administration. The specific duration should be discussed with the healthcare provider or medical professional administering the IV Ativan, as they will consider the individual’s condition and medical needs.
How fast does Ativan work for anxiety?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically starts to work for anxiety within 30 minutes to 1 hour after taking it, although some individuals may experience a quicker onset of effects. The speed of its action can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s metabolism and food in the stomach.
How long does it take for Ativan to kick in?
Ativan (lorazepam) usually begins to take effect within about 30 minutes to 1 hour after it is taken. However, the onset of action can vary from person to person, and it may be influenced by factors such as the individual’s metabolism and whether the medication is taken with or without food.
Ativan Overdose
Ativan overdose may happen at any level higher than what your doctor has prescribed for you. The amount of Ativan a person takes to reach an Ativan overdose differs from person to person. This can be based on weight, gender, genetics, and underlying health conditions, among other factors. The doctor prescribing a person Ativan considers these factors when deciding what dose is safe.
Since Ativan is highly potent and can appear harmless as a prescription drug, it may cause both accidental and intentional abuse as well as an accidental Ativan overdose. Most commonly, overdoses happen when it is taken in combination with alcohol or other drugs.
Primary signs of Ativan overdose may include the following:
- Mental confusion.
- Slurred speech.
- Lack of energy.
- Loss of control of body movements.
- Muscle weakness.
- Low blood pressure.
- Slow breathing.
- Passing out.
- Coma.
Severe Ativan overdose cases can be fatal when combined with other drugs.
Ativan Overdose Symptoms
Ativan is a benzodiazepine drug prescribed to treat anxiety and seizures. Ativan should only be taken as directed by a doctor and can be dangerous in large doses. Overdosing on Ativan can lead to severe medical complications, including cardiac arrest and respiratory failure. If you or someone you know may have taken too much Ativan, seek immediate medical help.
Additional symptoms of an Ativan overdose can include:
- Confusion.
- Slurred speech.
- Slowed breathing,
- Sedation.
- Coma.
- Even death.
An Ativan overdose can lead to other long-term physical and psychological effects. These may include an increased risk of depression, trouble sleeping, and memory problems. These effects of Ativan may last for weeks or months, even after the Ativan has been eliminated from the body.
If you believe you may have overdosed on Ativan, seek immediate medical attention.
How Much Ativan to Overdose?
Are you wondering how much Ativan to overdose, or what dose is required for an Ativan overdose? The exact amount of Ativan needed to overdose varies from person to person. Generally speaking, it is possible to overdose on as little as 4 mg of Ativan, but this could vary depending on an individual’s tolerance, health condition, and other factors. It is necessary to follow a doctor’s instructions when taking Ativan.
Ativan Overdose Reversal Treatments
Ativan overdose reversal usually occurs with clinical care, such as stomach pumping, activated charcoal, flumazenil, and supportive care, such as IV fluids. If medical help is not sought, the effects of an Ativan overdose may include agitation, confusion, coma, and respiratory depression.
Ativan Overdose Treatment Ems
Treatment for an Ativan overdose will depend on the severity of the overdose. Generally, emergency responders will provide oxygen, fluids, and medication to stabilize the person’s breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Activated charcoal may also be given to reduce the amount of Ativan in the body. The person will also be monitored closely; treatment may include psychological and social support.
Antidote for Ativan Overdose
Ativan is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, so the goal of any treatment for an Ativan overdose is to provide supportive care and reduce the amount of Ativan in the blood. Activated charcoal is the main antidote for an Ativan overdose, as it binds to the medication and prevents it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. It is vital to seek emergency medical care promptly if an Ativan overdose is suspected.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline (877) 378-4154Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
Side Effects of Ativan Infographic
It is important to remember that a physician prescribes this medication because they believe that its benefits are greater than the possible side effects. Most people who use this medication do not have severe side effects.
Embed the above “Ativan Side Effects” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/ativan-side-effects/
Ativan Side Effects image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Ativan-Side-Effects-min.png
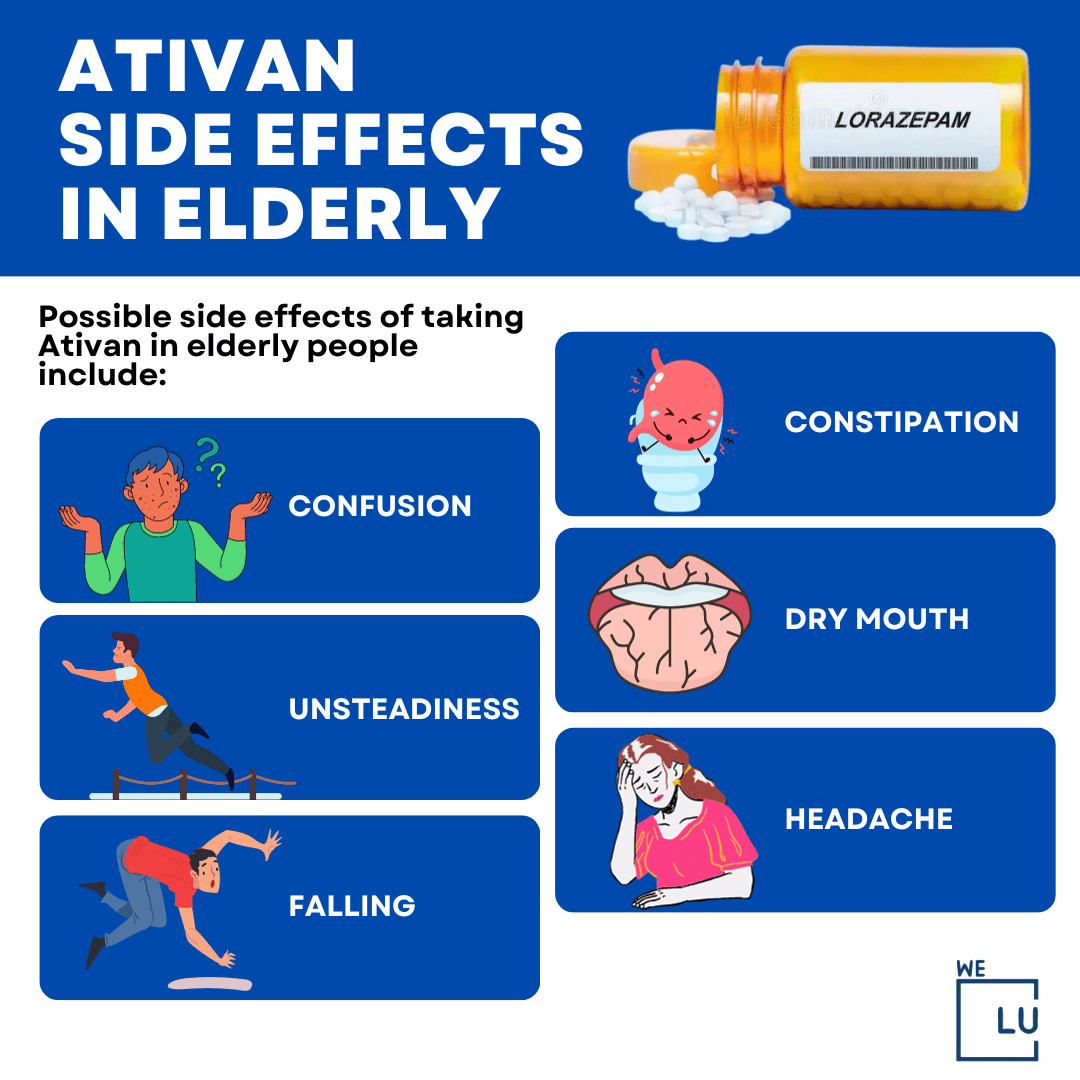
Embed the above “Ativan Side Effects in Elderly” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/ativan-side-effects/
Ativan Side Effects in Elderly image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Ativan-Side-Effects-in-Elderly-min.png
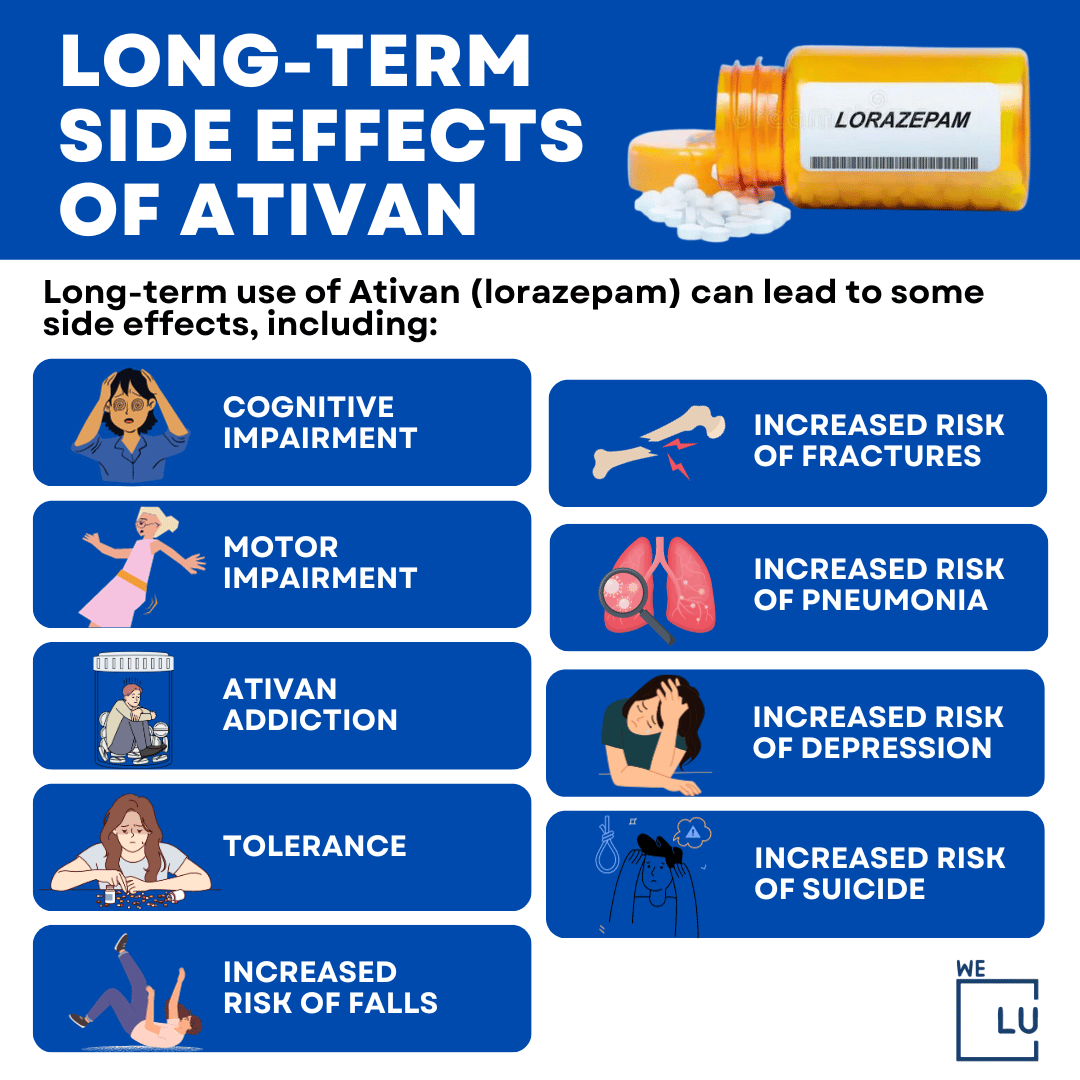
Embed the above “Long Term Side Effects of Ativan” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupnj.com/addiction/ativan-side-effects/
Long Term Side Effects of Ativan image link: https://welevelupnj.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Long-Term-Side-Effects-of-Ativan-min.png
Ativan Side Effects Withdrawal
Common Ativan withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, restlessness, tiredness, tremors, sweating, and increased heart rate.

Common Ativan withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, restlessness, tiredness, tremors, sweating, and increased heart rate.
Ativan and Alcohol Interaction
Even though Ativan is a prescription medication, it can be abused. One of the substances often abused with benzodiazepines such as Ativan is alcohol. This combination is dangerous because Ativan and alcohol depress the central nervous system and can lead to slowed breathing, extreme drowsiness, coma, and death.
Since Ativan and alcohol have similar effects on the brain and body, ingesting both within the same timeframe can heighten those effects, sometimes with deadly consequences. They both inhibit the central nervous system and can lower heart rate and breathing. The effects of the two combined can be greater than if they were consumed alone. The combination can cause severe drowsiness, breathing problems, coma, and death.
Ativan and Klonopin Interactions
Drug interactions are reported among people who take Ativan and Clonazepam (Klonopin). Typical interactions include weight decrease among females and depression among males. Using Ativan with Klonopin may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impaired thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with these medications.
Ativan and Adderall Drug Interactions
Adderall speeds the system up to help those with ADD or ADHD concentrate better and stay more alert. Unfortunately, some people mix Ativan and Adderall. Mixing drugs is a way for people to extend the high they feel or prevent withdrawal symptoms from other drugs they might be taking.
Adderall and Ativan are prescription medications that are prescribed for opposing purposes. Ativan slows the central nervous system’s response to stress and uncomfortable situations so that a person will have less anxiety. However, mixing Adderall and Ativan is dangerous because it increases the risk of an overdose. Other health problems can be caused by this combination, too.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL (877) 378-4154End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Ativan Side Effects and Addiction Treatment
There is a strong link between mental health and substance abuse. Individuals who struggle with mood disorders like depression and anxiety are more susceptible to developing an addiction to drugs or alcohol, often to self-medicate symptoms of their underlying mental health condition. These co-occurring disorders can make each other worse without proper treatment.
To determine the most effective ways to treat the Ativan side effects and addiction, getting an accurate assessment of all the symptoms is crucial. When a mental health professional has evaluated the symptoms, it may be determined that another form of mental condition is present and needs a particular type of treatment. Very often, some combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes are effective for coping with functional.
Medically-Assisted Ativan Detox
Detox is often considered the first stage of treatment. It will help you navigate the complicated withdrawal process but doesn’t address patterns of thought and behavior contributing to Ativan abuse. Various treatment approaches and settings can help provide the ongoing support necessary to maintain long-term sobriety after you complete detox.
Cravings are very common during detox and can be challenging to overcome. This often leads to relapse. Constant medical care provided during inpatient treatment helps prevent relapse. Clinicians can provide the necessary medication and medical expertise to lessen cravings and the effects of Ativan withdrawals.
Psychotherapy for Anxiety
Several different modalities of psychotherapy have been used in the treatment of anxiety and Ativan abuse, including the following:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: CBT is an effective treatment that involves changing both the patterns of negative thoughts and the behavioral routines that are affecting the daily life of the depressed person for various forms of depression.
- Person-Centered Therapy: A strategy that allows and encourages clients to understand and resolve their concerns in a safe, supportive environment.
- Solution Focused Therapy: An approach interested in solutions that can be quickly implemented with a simple first step leading to further positive consequences.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment for Ativan Abuse
Substance abuse and mental health disorders often co-occur. Traumatic experiences can often result in mental health disorders and substance abuse. Dual-diagnosis rehabilitation treats both of these issues together. The best approach for the treatment of dual diagnosis is an integrated system. This strategy treats both the substance abuse problem and the mental disorder simultaneously. Regardless of which diagnosis (mental health or substance abuse problem) came first, long-term recovery will depend mainly on the treatment for both disorders done by the same team or provider.
Medication-Assisted Treatments for Ativan Side Effects and Abuse
Medication-assisted treatments (MAT) for substance use disorders and mental health disorders are commonly used in conjunction. This includes the use of medications and other medical procedures. During your rehab, the staff from your treatment facility will help you identify what caused your addiction and teach you skills that will help you change your behavior patterns and challenge the negative thoughts that led to your addiction. Sometimes, the pressures and problems in your life make you rely on substances to help you forget about them momentarily.
If you or a loved one are struggling with long-term substance abuse and a co-occurring mental health condition such as anxiety and depression, contact one of our helpful treatment specialists today. The We Level Up New Jersey Ativan addiction center can provide information on dual diagnosis and detox programs that may fit your needs.
Overcoming Ativan Side Effects. Find the Support You Need.
Ativan side effects from abuse or dependency are often challenging to go through alone.
Many people experience relapses during withdrawal in an attempt to alleviate symptoms and satisfy cravings. However, you can manage withdrawal symptoms and successfully recover with detox and rehab therapy and a robust support system at the We Level Up New Jersey treatment center.
If you require assistance with your rehab journey, contact a We Level Up NJ treatment professional now. Your call is free and confidential.
Get a free rehab insurance check without any obligation.
Top 20 Most Common Ativan Side Effects FAQs
Does Ativan lower blood pressure?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can lower blood pressure as one of its potential side effects. It is a central nervous system depressant that can cause relaxation and reduced heart rate, which may decrease blood pressure.
How long does Ativan effects last?
The effects of Ativan (lorazepam) generally last for about 6 to 8 hours. However, the duration of Ativan side effects can vary from person to person, and factors like the dose taken, individual metabolism, and overall health can influence how long the drug remains active in the body.
Is Ativan the same as Xanax?
No, Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam) are not the same medications, although they both belong to the benzodiazepine class of drugs and are used to treat anxiety and certain other conditions. They have different chemical structures, potencies, and durations of action, and their dosages and Ativan side effects can vary. Take these medications only as a healthcare professional prescribes and not interchange them without medical guidance due to their differences in potency and dosing.
Is Ativan a benzodiazepine?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) is a benzodiazepine medication. It belongs to the benzodiazepine class of drugs, known for their sedative, anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), and muscle relaxant properties. It is commonly prescribed for conditions like anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
How long for Ativan to work?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically begins to work relatively quickly, usually within 30 minutes to an hour after oral administration. The onset of Ativan side effects can vary from person to person based on factors such as metabolism and whether it’s taken with or without food.
Is Ativan addictive like Xanax?
Yes, Ativan (lorazepam) can be addictive, much like Xanax (alprazolam). Both medications belong to the benzodiazepine class, which has the potential for dependence and addiction if misused or for an extended period. It’s crucial to take these medications only as a healthcare professional prescribes and follow their guidance to minimize the risk of addiction and withdrawal symptoms.
Can you snort Ativan?
Snorting Ativan (lorazepam) is not recommended and can be dangerous. Ativan is intended to be taken orally as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Snorting it can lead to rapid and unpredictable absorption, potentially increasing the risk of side effects and harmful consequences, including damage to the nasal passages. It’s essential to use medication only as directed by a medical professional to avoid potential Ativan side effects.
Does Ativan expire?
Like all medications, Ativan (lorazepam) has an expiration date, typically printed on the packaging. It’s crucial to adhere to the expiration date and not use Ativan or any expired medication, as its effectiveness and safety may be compromised.
How long do Ativan effects last?
The effects of Ativan (lorazepam) typically last for about 6 to 8 hours. However, individual variations, dosage, and factors like metabolism can influence how long the effects are felt. Follow the prescribed dosing instructions and not take Ativan for longer or in higher doses than a healthcare provider recommends to minimize the risk of dependence and other potential Ativan side effects.
Is Klonopin stronger than Ativan?
Klonopin (clonazepam) is generally considered longer-acting and may have a more prolonged action duration than Ativan (lorazepam). They are often considered to be of similar strength in terms of potency. Still, individual responses can vary, so using these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can determine the most appropriate treatment for your needs is essential.
What does Ativan look like?
Ativan (lorazepam) is available in various forms and can look different depending on the manufacturer and dosage. It commonly comes in tablet form, with different colors and markings depending on the strength. Check the packaging and labeling to ensure you have the correct medication and dosage as your healthcare provider prescribes.
How long does Ativan take to kick in?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically begins to take effect relatively quickly, usually within 30 minutes to an hour after oral administration. However, the onset of Ativan side effects can vary depending on factors like individual metabolism and whether it is taken on an empty or full stomach.
How long does Ativan stay in your urine?
The detection window for Ativan (lorazepam) in urine can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use. Generally, it can be detected in urine for approximately 3 to 6 days after the last dose, but it may be detectable for a longer or shorter duration in some cases.
What is the half life of Ativan?
The half-life of Ativan (lorazepam) typically ranges from 10 to 20 hours, with an average of about 12 hours in most individuals. This means it takes back this time for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body, but it may vary depending on factors like age, liver function, and overall health.
Can you sniff Ativan?
You should not sniff or snort Ativan (lorazepam) or other medication. Ativan is intended to be taken orally as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Snorting it can lead to rapid absorption, potentially increasing the risk of Ativan side effects and harmful consequences, including damage to the nasal passages. Always use medication as a medical professional directs to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How long does it take for Ativan to work?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically begins to work relatively quickly, often within 30 minutes to an hour after oral administration. The onset of Ativan side effects can vary from person to person. It may depend on factors such as the individual’s metabolism and whether the medication is taken on an empty or full stomach.
Is Ativan stronger than Xanax?
The relative strength of Ativan (lorazepam) compared to Xanax (alprazolam) can vary from person to person. In general, they are of similar potency. Still, individual responses may differ, so using these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can determine the most appropriate treatment for your needs is essential.
What is Ativan used for?
Ativan (lorazepam) primarily treats anxiety disorders, including generalized and panic disorders. It can also be prescribed for the short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety and anxiety associated with depression and for managing certain medical conditions, such as insomnia, seizures, and alcohol withdrawal.
How long does it take Ativan to work?
Ativan (lorazepam) typically begins to work relatively quickly, usually within 30 minutes to an hour after taking it orally. However, the onset of the Ativan side effects can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s metabolism and whether it is taken on an empty or full stomach.
How long do the effects of Ativan last?
The effects of Ativan (lorazepam) typically last for about 6 to 8 hours. However, the duration of Ativan side effects can vary depending on factors like the dosage, individual metabolism, and overall health. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosing instructions and not take Ativan for longer or in higher doses than a healthcare provider recommends to minimize the risk of dependence and other potential Ativan side effects.
Ativan Side Effects Video
Dive into the comprehensive guide on Ativan Side Effects and Drug Risks. Whether you’re prescribed Ativan or know someone who is, understanding its potential impacts is crucial. Here’s what you need to know:
Prescription Drug Abuse, Prescription Medication Addiction Recovery, and Sobriety Story Video.
Ativan prescription drug abuse can lead to various side effects, including physical and psychological dependence, drowsiness, confusion, and even respiratory depression in severe cases. However, sobriety is possible with the right help and support. Suppose you or someone you know struggles with Ativan or prescription drug abuse. In that case, seek assistance from a healthcare provider, counselor, or addiction specialist who can guide you through recovery.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers various recovery programs at each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up NJ Ativan Side Effects Detox, Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] NIH – https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682053.html Ativan side effects
[2] NCBI – https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lorazepam and ativan side effects facts
[3] Ambien (zolpidem tartrate) tablets, for oral use, C-IV. (2022).
https://products.sanofi.us/ambien/ambien.pdf
[4] Ativan (lorazepam) tablets. (2021).
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/017794s048lbl.pdf Ativan side effects data sheets.
[5] Ativan injection (lorazepam injection, USP). (2021).
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/18140s046lbl.pdf Ativan side effects from injections.
[6] Klonopin tablets (clonazepam). (2021).
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/017533s061lbl.pdf
[7] Schutte-Rodin, S., et al. (2008). Clinical guideline for evaluating and managing chronic insomnia in adults vs Ativan side effects.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2576317/
[8] Valium brand of diazepam tablets. (2021).
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/013263s096lbl.pdf
[9] Xanax (alprazolam) tablets for oral use, CIV. (2021).
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/018276s055lbl.pdf
[10] Wu, W., et al. (2016). Lorazepam or diazepam for convulsive status epilepticus: A meta-analysis.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0967586815007043